Using computer simulations of a model by U.S. Nobel Laureate William Nordhaus, researchers have weighted climate damage from increasing weather extremes, decreasing labor productivity and other factors against the costs of cutting greenhouse gas emission by phasing out coal...
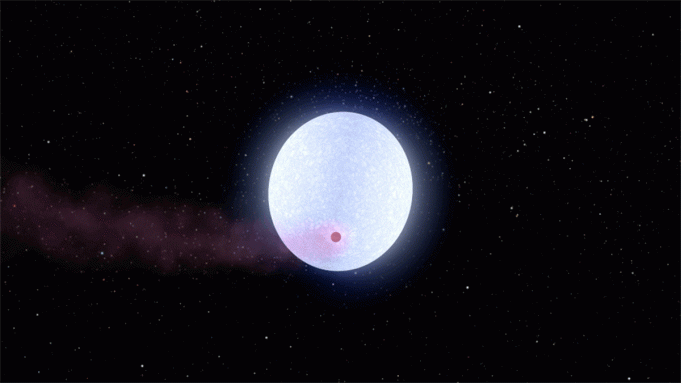
In the scorching atmosphere of exoplanet KELT-9b, even molecules are torn to shreds.
Massive gas giants called "hot Jupiters"—planets that orbit too close to their stars to sustain life—are some of the strangest worlds found beyond our solar system. New observations show...
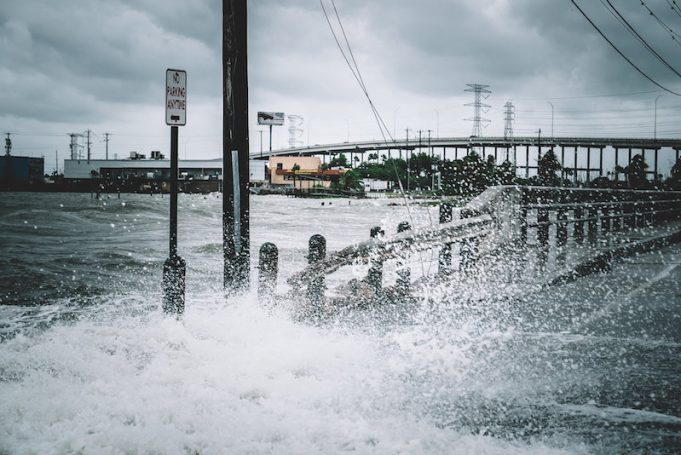
When Hurricane Harvey slammed into the Texas coast in 2017, displaced residents flocked inland, trying to rebuild their lives in the disaster's aftermath. Within decades, the same thing could happen at a much larger scale due to rising sea...
Scientists for the first time have developed a single molecule that can absorb sunlight efficiently and also act as a catalyst to transform solar energy into hydrogen, a clean alternative to fuel for things like gas-powered vehicles.
This new molecule...
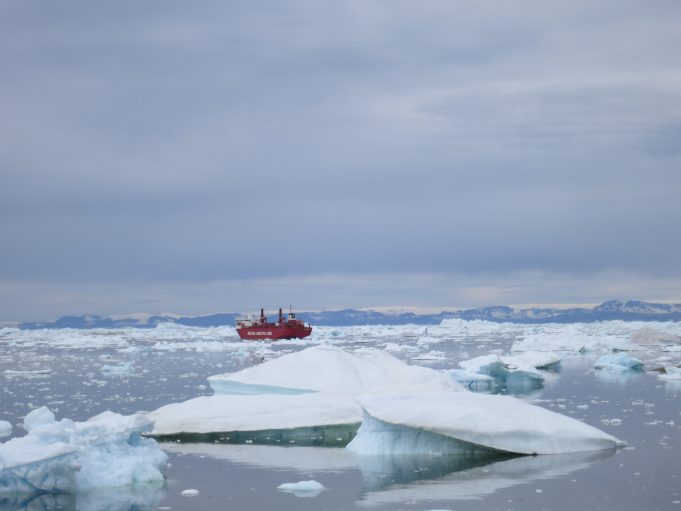
Limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees C requires a decarbonized world by 2050 at the latest, and a corresponding global transformation of the energy and land use systems of societies around the world. To achieve this goal...
A scientific paper published in 1985 was the first to report a burgeoning hole in Earth's stratospheric ozone over Antarctica. Scientists determined the cause to be ozone-depleting substances—long-lived artificial halogen compounds. Although the ozone-destroying effects of these substances are...
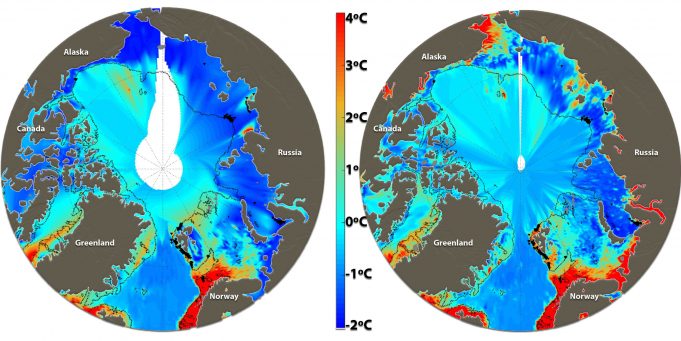
The atmospheric concentration of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, has almost tripled since the beginning of industrialisation. Methane emissions from natural sources are poorly understood. This is especially the case for emissions from the Arctic Ocean.
The Arctic Ocean is...
Global warming, a major aspect of climate change, is already causing a wide range of negative impacts on many habitats of our planet. It is thus of the utmost importance to understand how rising temperatures may affect animal health...
New research from the University of California San Diego finds that solar geoengineering—the intentional reflection of sunlight away from the Earth's surface—may reduce income inequality between countries.
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, researchers examine the impacts of solar...
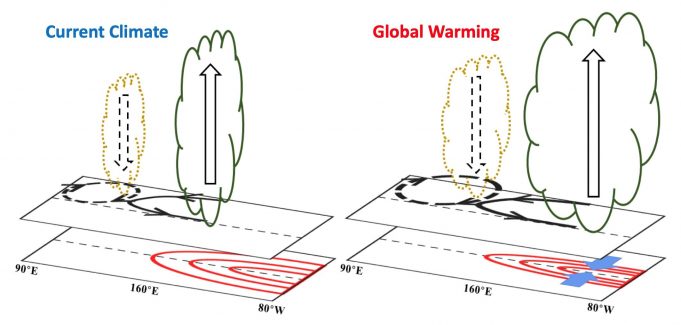
El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is the strongest signal in interannual climate variation. El Niño increases the precipitation over the equatorial central-eastern Pacific, which releases more latent heat into the tropical atmosphere and thus drives variations of the global climate...
A new study published by biologists at LMU demonstrates that there are no simple or universal solutions to the problem of engineering plants to enable them to cope with the challenges posed by climate change.
For plants, climate change promises one...