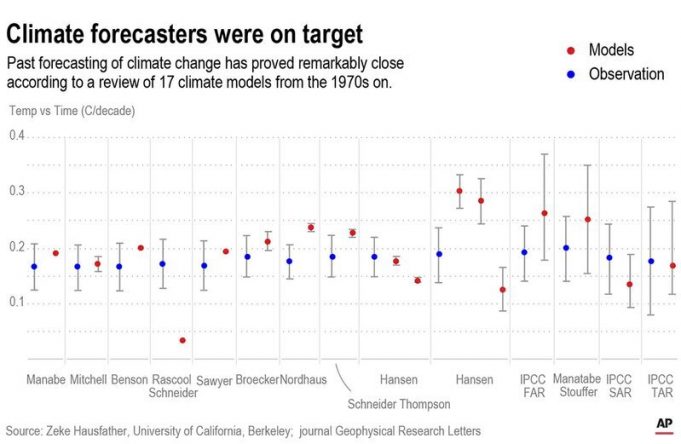
The computer models used to simulate what heat-trapping gases will do to global temperatures have been pretty spot-on in their predictions, a new study found.
After years of hearing critics blast the models' accuracy, climate scientist Zeke Hausfather decided to...
Volcanic eruptions, not natural variability, were the cause of an apparent "Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation," a purported cycle of warming thought to have occurred on a timescale of 40 to 60 years during the pre-industrial era, according to a team...
Chi Chen, a Boston University graduate researcher, and Ranga Myneni, a BU College of Arts & Sciences professor of earth and environment, released a new paper that reveals how humans are helping to increase the Earth's plant and tree...
The largest study ever conducted of its kind has identified where and how to save coral reef communities in the Indo-Pacific, according to an international group of scientists from WCS (Wildlife Conservation Society) and other conservation NGOs, government agencies,...
University of Southampton scientists investigating ways of removing carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases from our atmosphere believe volcanic ash could play an important role.
A team from the University's School of Ocean and Earth Science has modeled the...
A major shift in western Arctic wind patterns occurred throughout the winter of 2017 and the resulting changes in sea ice movement are possible indicators of a changing climate, says Kent Moore, a professor of physics at the University...
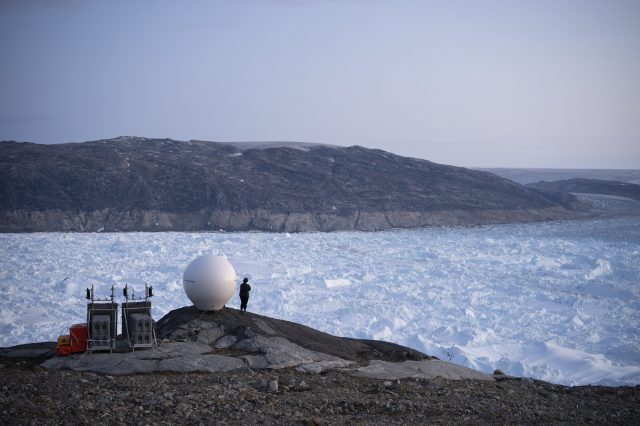
Greenland lost a record amount of ice during an extra warm 2019, with the melt massive enough to cover California in more than four feet (1.25 meters) of water, a new study said.
After two years when summer ice melt...
Species have few good options when it comes to surviving climate change—they can genetically adapt to new conditions, shift their ranges, or both.
But new research in PNAS indicates that conflicts between species as they adapt and shift ranges could lead experts...
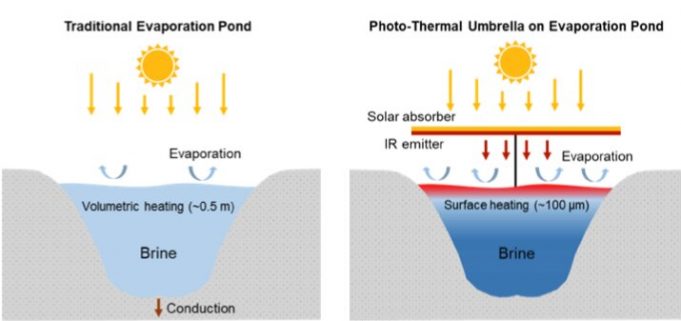
Evaporation ponds, which are commonly used in many industries to manage wastewater, can span acres, occupying a large footprint and often posing risks to birds and other wildlife. Yet they're an economical way to deal with contaminated water because...
Physical climate risk from extreme weather events remains unaccounted for in financial markets. Without better knowledge of the risk, the average energy investor can only hope that the next extreme event won't trigger a sudden correction, according to new...
"Zombie fires" and burning of fire-resistant vegetation are new features driving Arctic fires—with strong consequences for the global climate—warn international fire scientists in a commentary published in Nature Geoscience.
The 2020 Arctic wildfire season began two months early and was unprecedented...