Nanodiamonds were first discovered in the 1960s and are microscopic crystals—or regions of crystals—that display the same carbon-atom lattice that macro-scale diamonds do. They are made under heat and high pressure from detonations and are used for electronics applications....
Engineers have discovered a new way of generating electricity using tiny carbon particles that can create a current simply by interacting with liquid surrounding them.
The liquid, an organic solvent, draws electrons out of the particles, generating a current that could...
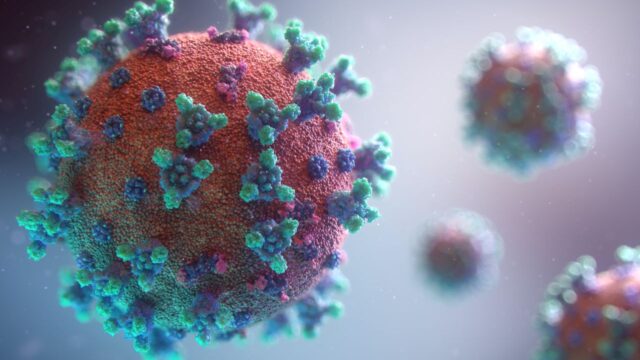
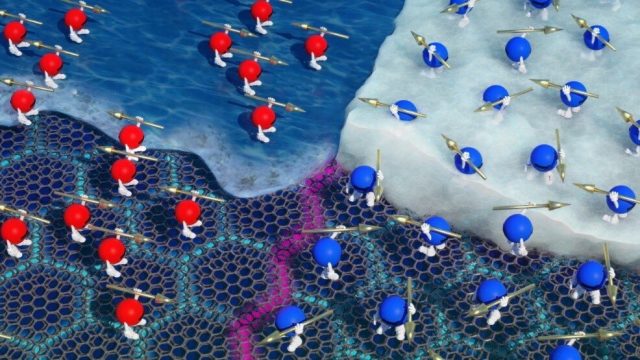
Researchers led by ETH Zurich have developed a new water filter membrane that is both highly effective and environmentally friendly. The membrane eliminates a wide range of water-borne viruses, H1N1 flu viruses and even the new SARS-CoV-2 virus from...
Scientists discover a new allotrope of carbon that is similar to graphene. As with graphene, it is only one atom thick. However, unlike graphene, it behaves like metals even on a small scale. A perfect fit for nanosized wires....
In work that could turn cell phones into sensors capable of detecting viruses and other minuscule objects, MIT researchers have built a powerful nanoscale flashlight on a chip.
Their approach to designing the tiny light beam on a chip could also be...
Australian researchers have identified neutralising nanobodies that block the SARS-CoV-2 virus from entering cells in preclinical models.
The discovery paves the way for further investigations into nanobody-based treatments for COVID-19.
Published in PNAS, the research is part of a consortium-led effort, bringing...
New FLEET research confirms the potential for topological materials to substantially reduce the energy consumed by computing.
The collaboration of FLEET researchers from University of Wollongong, Monash University and UNSW have shown in a theoretical study that using topological insulators...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Graphene excels at removing contaminants from water, but it's not yet a commercially viable use of the wonder material.
That could be changing.
In a recent study, University at Buffalo engineers report a new process of 3D printing...
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology discover a surprising phase transition in twisted bilayer graphene.
Most materials go from being solids to liquids when they are heated. One rare counter-example is helium-3, which can...
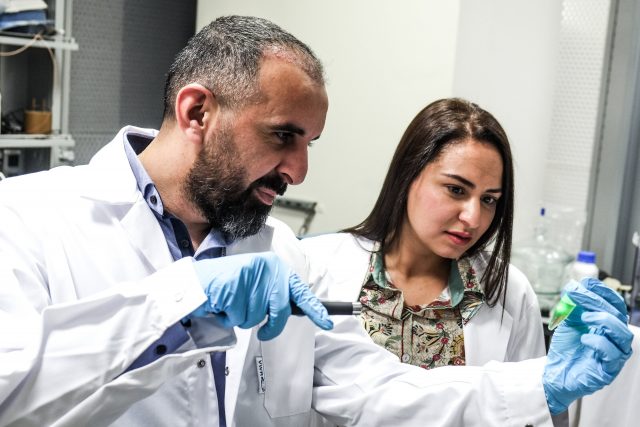
A revolutionary technology developed within the Trabolsi Research Group at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) could dramatically improve the wellbeing of diabetic patients: an insulin oral delivery system that could replace traditional subcutaneous injections without the side effects caused by...
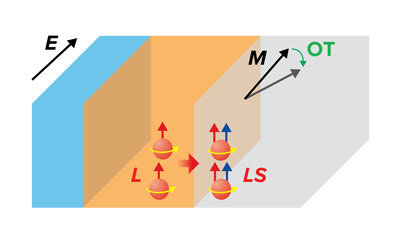
The development of innovative magnetic nanodevices is one step closer to reality thanks to the observation by RIKEN physicists of a type of rotation that can be realized in materials consisting of light elements.
The ability to use electric currents to turn...