An international team of scientists has defied nature to make diamonds in minutes in a laboratory at room temperature—a process that normally requires billions of years, huge amounts of pressure and super-hot temperatures.
The team, led by The Australian National...
A group of researchers led by Sir Andre Geim and Dr Alexey Berdyugin at The University of Manchester have discovered and characterised a new family of quasiparticles named 'Brown-Zak fermions' in graphene-based superlattices.
The team achieved this breakthrough by aligning...
'I've worked in this field for more than 10 years and have not seen anything like this.'
A new synthetic protein nanoparticle capable of slipping past the nearly impermeable blood-brain barrier in mice could deliver cancer-killing drugs directly to malignant...
Nanographene is a material that is anticipated to radically improve solar cells, fuel cells, LEDs and more. Typically the synthesis of this material has been imprecise and difficult to control. For the first time, researchers have discovered a simple...
The University of Nottingham has cracked the conundrum of how to use inks to 3D-print novel electronic devices with useful properties, such as an ability to convert light into electricity.
The study shows that it is possible to jet inks,...
Plastic waste comes back in black as pristine graphene, thanks to ACDC.
That's what Rice University scientists call the process they employed to make efficient use of waste plastic that would otherwise add to the planet's environmental woes. In this...
As progress in traditional computing slows, new forms of computing are coming to the forefront. At Penn State, a team of engineers is attempting to pioneer a type of computing that mimics the efficiency of the brain's neural networks...
Newly developed biosensor devices linked to smartphones could help medical practitioners dramatically cut down the real-time detection rates in the battle against COVID-19 and other future viral outbreaks.
Scientists and engineers from the University of Manchester have created a novel computational...
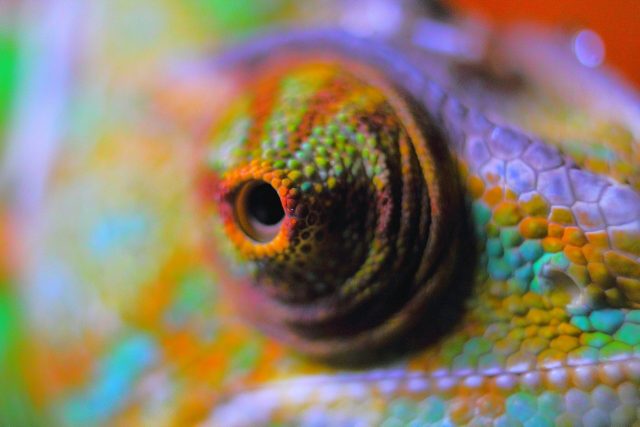
Chameleons can famously change their colors to camouflage themselves, communicate and regulate their temperature. Scientists have tried to replicate these color-changing properties for stealth technologies, anti-counterfeiting measures and electronic displays, but the materials have limitations. Now, researchers have developed...
Imagine a mobile phone charger that doesn't need a wireless or mains power source. Or a pacemaker with inbuilt organic energy sources within the human body.
Australian researchers led by Flinders University are picking up the challenge of "scavenging" invisible...
Since the discovery of graphene more than 15 years ago, researchers have been in a global race to unlock its unique properties. Not only is graphene—a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon arranged in a hexagonal lattice—the strongest, thinnest material known...