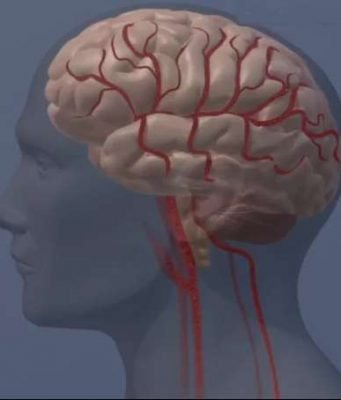
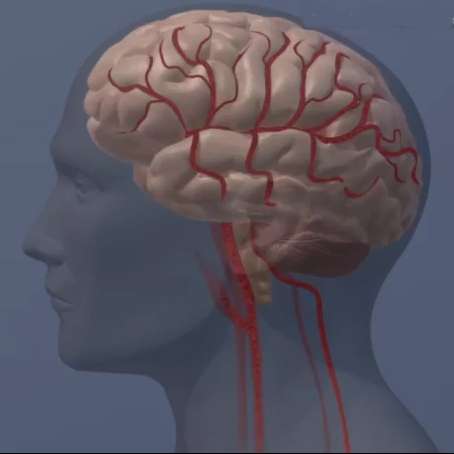
MIT neuroscientists have developed a new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sensor that allows them to monitor neural activity deep within the brain by tracking calcium ions.
Because calcium ions are directly linked to neuronal firing—unlike the changes in blood flow...
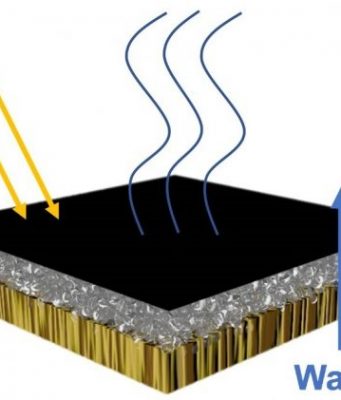
The ever-more-humble carbon nanotube may be just the device to make solar panels—and anything else that loses energy through heat—far more efficient.
Rice University scientists are designing arrays of aligned single-wall carbon nanotubes to channel mid-infrared radiation(aka heat) and greatly raise the...
Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Engineering have developed a battery anode based on a new nanostructured alloy that could revolutionize the way energy storage devices are designed and manufactured.
The zinc- and manganese-based alloy further opens the...
Wavelike, collective oscillations of electrons known as "plasmons" are very important for determining the optical and electronic properties of metals.
In atomically thin 2-D materials, plasmons have an energy that is more useful for applications, including sensors and communication devices,...
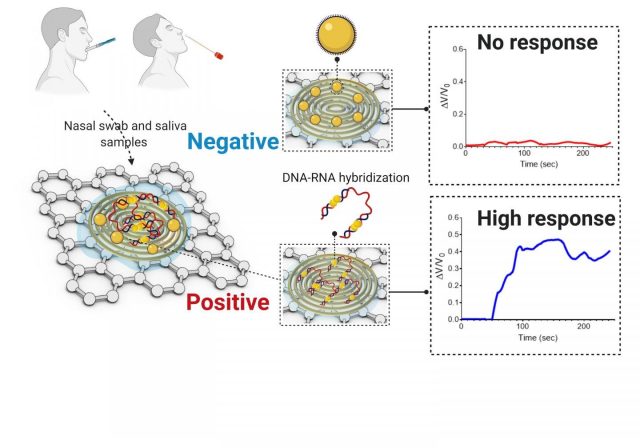
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the world, testing remains a key strategy for tracking and containing the virus. Bioengineering graduate student, Maha Alafeef, has co-developed a rapid, ultrasensitive test using a paper-based electrochemical sensor that can...
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed neutrophil "nanosponges" that can safely absorb and neutralize a variety of proteins that play a role in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Injections of these nanosponges effectively treated severe...
Rice University engineers have zeroed in on the optimal architecture for storing hydrogen in "white graphene" nanomaterials—a design like a Lilliputian skyscraper with "floors" of boron nitride sitting one atop another and held precisely 5.2 angstroms apart by boron...
Training neural networks to perform tasks, such as recognizing images or navigating self-driving cars, could one day require less computing power and hardware thanks to a new artificial neuron device developed by researchers at the University of California San...
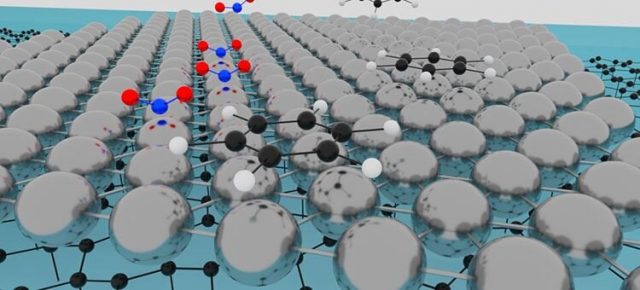
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, together with colleagues from other universities, have discovered the possibility to prepare one-atom thin platinum for use as a chemical sensor. The results were recently published in the scientific journal Advanced Material...
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, are attempting to convert carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, to fuel using energy from sunlight. Recent results have shown that it is possible to use their technique to selectively produce methane, carbon monoxide or...
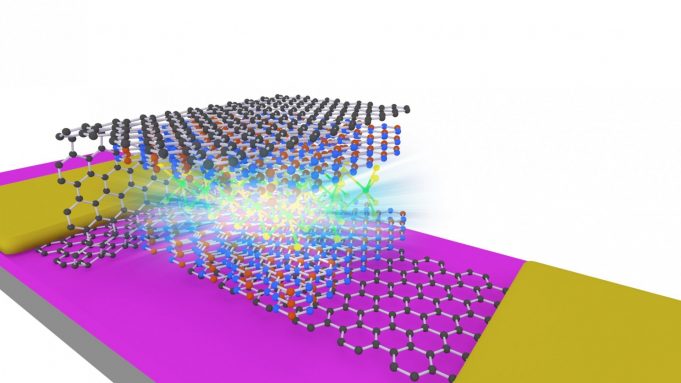
When atomically thin semiconductors are combined together in a Lego style, they emit light at a lower voltage potentially leading to low energy consumption devices.
Whilst this research is in its fundamental state this shows promise for practical applications in...