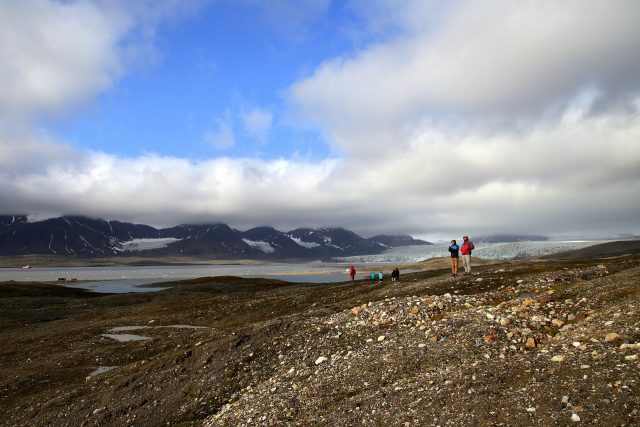
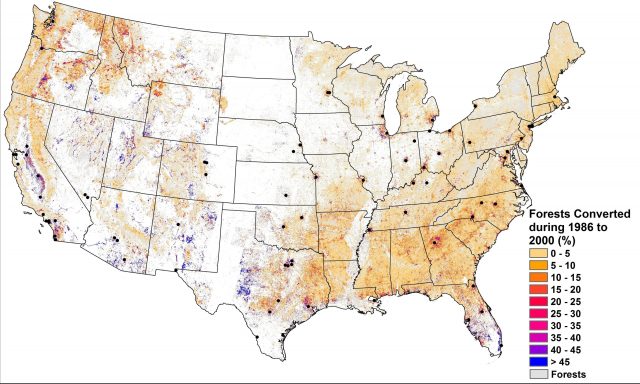
New research by Christopher A. Williams, an environmental scientist and professor in Clark University's Graduate School of Geography, reveals that deforestation in the U.S. does not always cause planetary warming, as is commonly assumed; instead, in some places, it...
New research shows that hurricane maximum wind speeds in the subtropical Atlantic around Bermuda have more than doubled on average over the last 60 years due to rising ocean temperatures in the region.
Hurricanes intensify by extracting energy from the...
The Columbia River basin will see an increase in flooding over the next 50 years as a result of climate change, new modeling from Oregon State University indicates.
The magnitude of flooding -- the term used to describe flooding severity...
Rising global temperatures are causing frozen Arctic soil -- permafrost -- in the northern hemisphere to thaw and release CO2 that has been stored within it for thousands of years. The amount of carbon stored in permafrost is estimated to...
Global greenhouse gas emissions over the last century have made southern China a hotspot for bat-borne coronaviruses, by driving growth of forest habitat favoured by bats.
A new study published today in the journal Science of the Total Environment provides the first...
If temperature varies strongly from day to day, the economy grows less. Through these seemingly small variations climate change may have strong effects on economic growth. This shows data analyzed by researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact...
Extensive sea ice covered the world's oceans during the last ice age, which prevented oxygen from penetrating into the deep ocean waters, complicating the relationship between oxygen and carbon, a new study has found.
"The sea ice is effectively like...
There are fossils, found in ancient marine sediments and made up of no more than a few magnetic nanoparticles, that can tell us a whole lot about the climate of the past, especially episodes of abrupt global warming. Now,...
The lockdowns and reduced societal activity related to the COVID-19 pandemic affected emissions of pollutants in ways that slightly warmed the planet for several months last year, according to new research led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research...
The researchers of the Institute for Atmospheric and Earth system research at the University of Helsinki have investigated how atmospheric particles are formed in the Arctic. Until recent studies, the molecular processes of particle formation in the high Arctic...
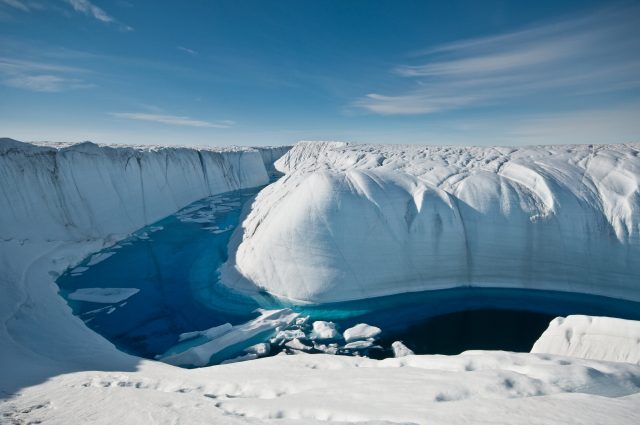
The rate at which ice is disappearing across the planet is speeding up, according to new research.
And the findings also reveal that the Earth lost 28 trillion tonnes of ice between 1994 and 2017 -- equivalent to a sheet...