Winds blowing across snow dunes on Antarctica's Ross Ice Shelf cause the massive ice slab's surface to vibrate, producing a near-constant set of seismic "tones" scientists could potentially use to monitor changes in the ice shelf from afar, according...
Peatlands are extremely effective at storing carbon, but an international study featuring a University of Queensland researcher has found climate change could stop that.
The group investigated how peatlands -- swamps and bogs with organic rich soils -- have responded...
The Baltic Sea is home to some of the world's largest dead zones, areas of oxygen-starved waters where most marine animals can't survive. But while parts of this sea have long suffered from low oxygen levels, a new study...
Increased water vapor in Earth's atmosphere due to human activities is making shimmering high-altitude clouds more visible, a new study finds. The results suggest these strange but increasingly common clouds seen only on summer nights are an indicator of...
Yosemite National Park contains some of the world's most iconic landforms, including Half Dome, Yosemite Falls, and El Capitan. Although the cliffs of Yosemite Valley may appear static, rockfalls from these cliffs are common, with a rockfall occurring every...
Scientists have developed a detailed analysis of how 22 recent hurricanes would be different if they formed under the conditions predicted for the late 21st century.
While each storm's transformation would be unique, on balance, the hurricanes would become a...
The first whole-genome analyses of ancient human DNA from Southeast Asia reveal that there were at least three major waves of human migration into the region over the last 50,000 years.
The research, published online May 17 in Science, complements...
In the weeks before Hurricane Harvey tore across the Gulf of Mexico and plowed into the Texas coast in August 2017, the Gulf's waters were warmer than any time on record, according to a new analysis led by the...
Concern over the potential imminent eruptions of Earth's supervolcanoes, like Taupo in New Zealand or Yellowstone in the United States, may be quelled by the results of a new study suggesting that geological signs pointing to a catastrophic eruption...
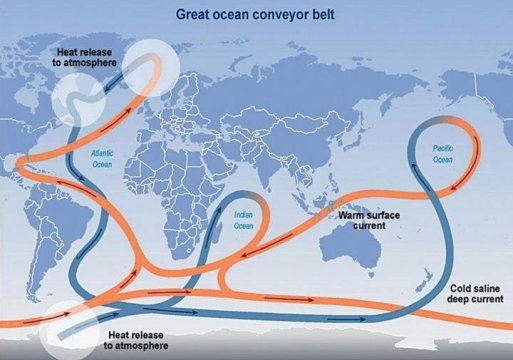
New research led by University College London (UCL) and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) provides evidence that a key cog in the global ocean circulation system hasn't been running at peak strength since the mid-1800s and is currently at...
James Cook University (JCU) scientists in Australia have found high carbon dioxide levels cause squid to bungle attacks on their prey.
PhD candidate Blake Spady from JCU's ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies led the investigation. He said...