A ground-breaking research study looking at modern and ancient landscapes has discovered African plants could be facing mass extinction faster than once thought.
Scientists from the Lyell Centre, Heriot-Watt University, looked at chemical fossils, with special emphasis on plant vegetable...
To stabilize the Earth's climate for people and ecosystems, it is imperative to ramp up natural climate solutions and, at the same time, accelerate mitigation efforts across the energy and industrial sectors, according to a new policy perspective published...
Strategies for limiting climate change must take into account their potential impact on water quality through nutrient overload, according to a new study from Carnegie's Eva Sinha and Anna Michalak published by Nature Communications. Some efforts at reducing carbon emissions...
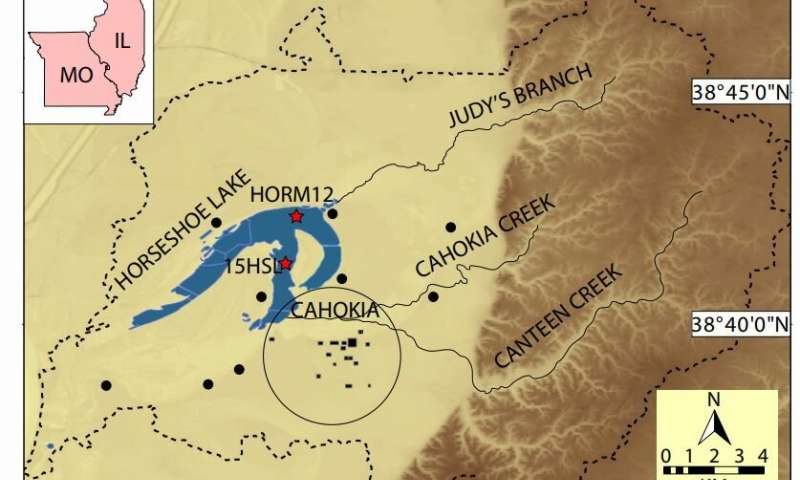
A new study shows climate change may have contributed to the decline of Cahokia, a famed prehistoric city near present-day St. Louis. And it involves ancient human poop.
Published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the...
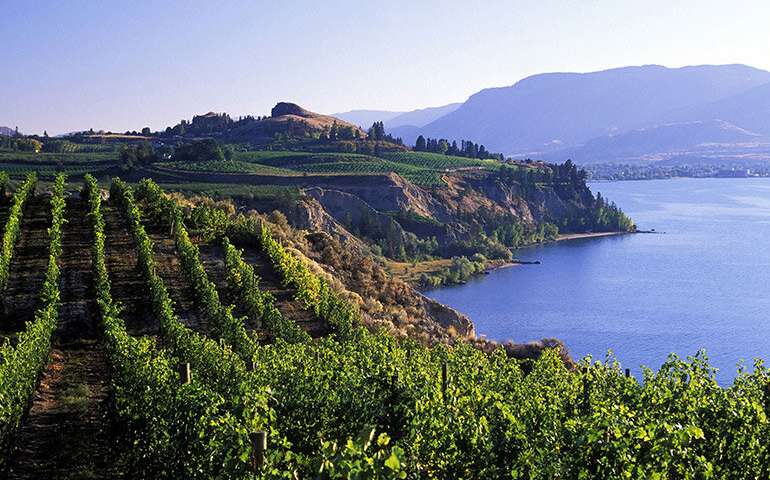
In a new study from UBC's Okanagan campus, researchers have discovered a surprising new source of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions—bicarbonates hidden in the lake water used to irrigate local orchards.
"We have been studying the carbon content of soil for some time,"...
A new study shows humans are pumping carbon dioxide into the atmosphere at a rate nine to 10 times higher than the greenhouse gas was emitted during a global warming event 56 million years ago that made the oceans...
More than half of the carbon sink in the world's forests is in areas where the trees are relatively young—under 140 years old—rather than in tropical rainforests, research at the University of Birmingham shows.
These trees have typically 'regrown' on...
Impacts from climate change are not always easy to see. But for many local businesses in coastal communities across the United States, the evidence is right outside their doors—or in their parking lots.
That evidence isn't just present in...
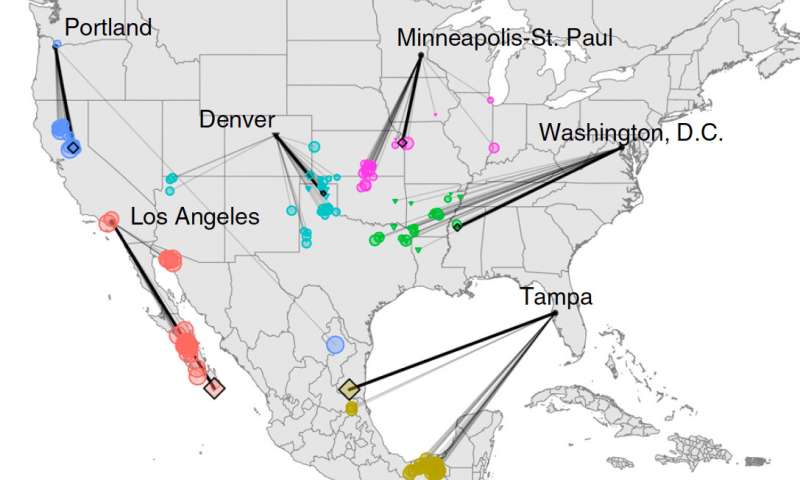
In one generation, the climate experienced in many North American cities is projected to change to that of locations hundreds of miles away—or to a new climate unlike any found in North America today.
A new study and interactive web...
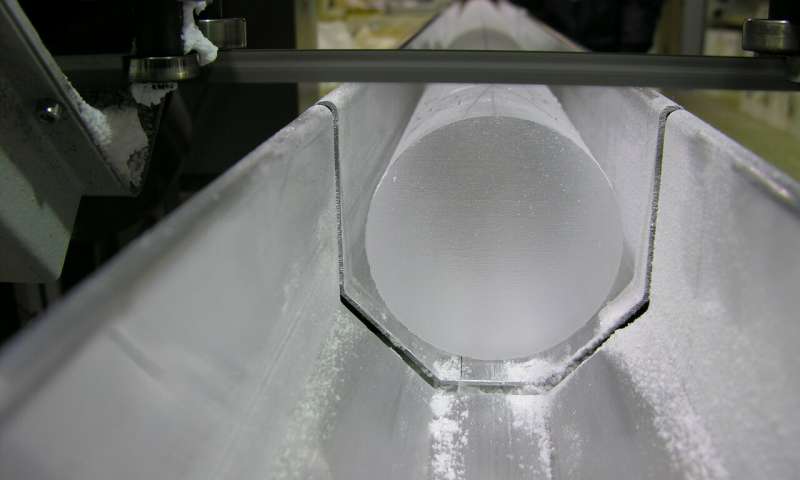
A new study on ice cores shows that reductions in sea ice in the Arctic in the period between 30-100,000 years ago led to major climate events. During this period, Greenland temperatures rose by as much as 16 degrees...
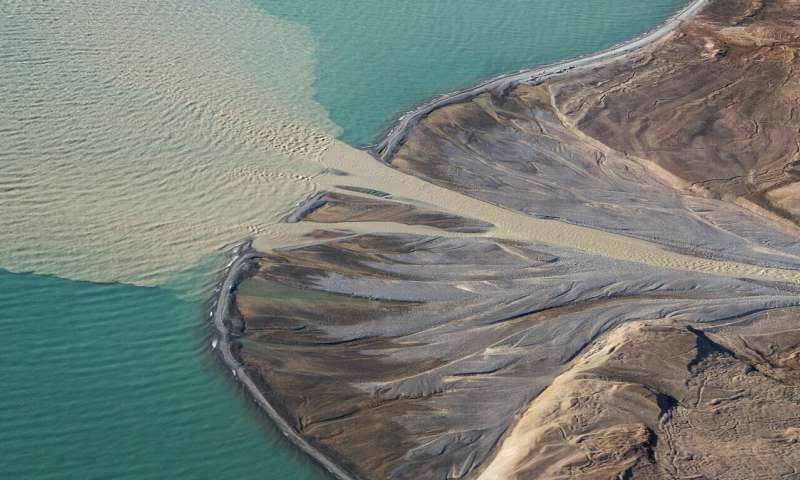
As climate change melts Greenland's glaciers and deposits more river sediment on its shores, an international group of researchers has identified one unforeseen economic opportunity for the Arctic nation: exporting excess sand and gravel abroad, where raw materials for...