Photosynthesis on Earth is regulated by plant phenology—how plant life cycles interact with the climate—and environmental conditions, both of which changed substantially in recent decades. Unlike early-season photosynthesis which is mostly driven by warming temperatures or the onset of...
Nations' failure to fulfil the promises they made in the Paris climate agreement to make drastic emissions cuts could cost the global economy as much as $600 trillion this century, new analysis showed Tuesday.
Under the landmark 2015 accord, countries...
In a new study, Stanford researchers have strongly bolstered the theory that a lack of oxygen in Earth's oceans contributed to a devastating die-off approximately 444 million years ago. The new results further indicate that these anoxic (little- to...
As agriculture emerged in early civilizations, crops were domesticated in four locations around the world—rice in China; grains and pulses in the Middle East; maize, beans and squash in Mesoamerica; and potatoes and quinoa in the Andes. Now, an...
A previously unknown significant source of carbon just discovered in the Arctic has scientists marveling at a once overlooked contributor to local coastal ecosystems—and concerned about what it may mean in an era of climate change.
In a Nature Communications paper released...
The American Dust Bowl of the 1930s—captured by the novels of John Steinbeck—was an environmental and socio-economic disaster that worsened the Great Depression.
The Dust Bowl was an extreme event. But due to climate change, massive crop failures are more likely...
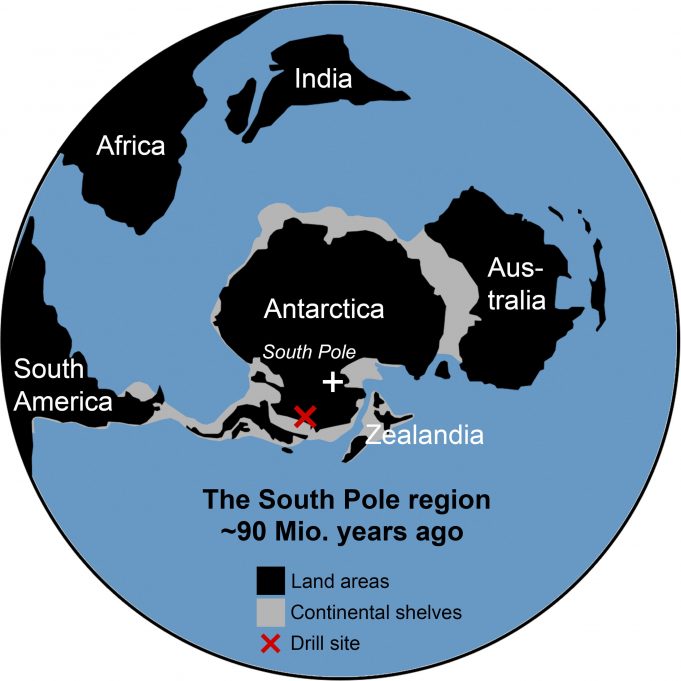
Researchers have found evidence of rainforests near the South Pole 90 million years ago, suggesting the climate was exceptionally warm at the time.
A team from the UK and Germany discovered forest soil from the Cretaceous period within 900 km...
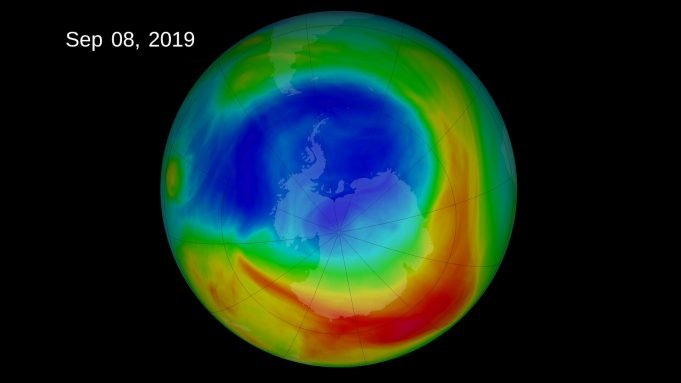
Chemicals that deplete Earth's protective ozone layer have also been triggering changes in Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation. Now, new research in Nature finds that those changes have paused and might even be reversing because of the Montreal Protocol, an international treaty...
Stratospheric aerosol geoengineering is the idea that adding a layer of aerosol particles to the upper atmosphere can reduce climate changes caused by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide.
Previous research shows that solar geoengineering could be achieved using commercially...
A new Stanford study reveals that a common scientific approach of predicting the likelihood of future extreme weather events by analyzing how frequently they occurred in the past can lead to significant underestimates—with potentially significant consequences for people's lives.
Stanford...
During the exceptionally warm Arctic summer of 2019, Greenland lost 600 billion tons of ice, enough to raise global sea levels by 2.2 millimeters in two months. On the opposite pole, Antarctica continued to lose mass in the Amundsen...