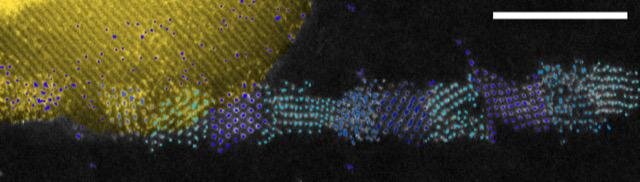
An international team has discovered that compressing monocrystalline (TaSe4)2I can create a system where the constituent TaSe4Q1-D atomic chains are in amorphous state without breaking the orientational and periodic translation symmetries of the chain lattice. Moreover, they found that...
A touch of gold—or another noble metal—can change the structure of a crystal and its intrinsic properties, physicists at the University of Warwick have demonstrated in a display of modern-day alchemy.
Scientists at the University of Warwick have found a...
Most people are familiar with uranium as a fuel for nuclear power plants. And while that's the most common application, this element is also used in many other fields, such as dyes, medical devices, and weapons. Scientists at EPFL's...
As levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide continue to climb, scientists are looking for new ways of breaking down CO2 molecules to make useful carbon-based fuels, chemicals and other products. Now, a team of Brown University researchers has found a way...
National University of Singapore chemists have developed a photo-induced method for late-stage functionalization of carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds in organic molecules.
The replacement of H in C-H bonds with other atoms or substituents is one of the most coveted ways to...
Tiny factories float inside our cells and provide them with almost all the energy they need: the mitochondria. Their effectiveness decreases when we get older, but also when we face many diseases such as diabetes, cancer or Parkinson's. This...
Chemical reactions driven by the geological conditions on the early Earth might have led to the prebiotic evolution of self-replicating molecules. Scientists at Ludwig-Maximilians Universitaet (LMU) in Munich now report on a hydrothermal mechanism that could have promoted the...
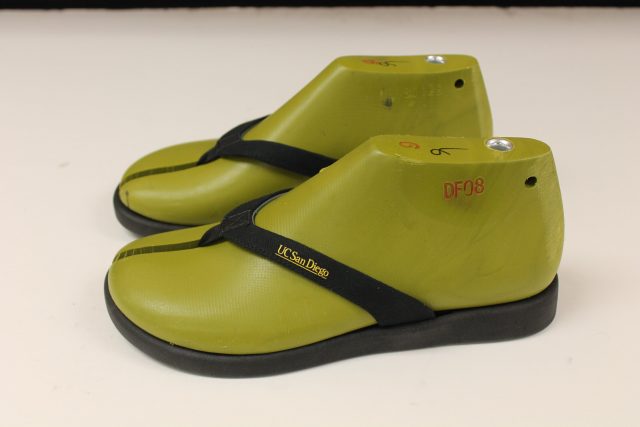
As the world's most popular shoe, flip-flops account for a troubling percentage of plastic waste that ends up in landfills, on seashores and in our oceans. Scientists at the University of California San Diego have spent years working to...
A machine-learning algorithm that can predict the compositions of trend-defying new materials has been developed by RIKEN chemists1. It will be useful for finding materials for applications where there is a trade-off between two or more desirable properties.
Artificial intelligence...
By formulating positively charged fluorescent dyes into a new class of materials called small-molecule ionic isolation lattices (SMILES), a compound's brilliant glow can be seamlessly transferred to a solid, crystalline state, researchers report August 6 in the journal Chem. The...
Need light but want privacy? A new type of wood that's transparent, tough, and beautiful could be the solution. This nature-inspired building material allows light to come through (at about 80%) to fill the room but the material itself...