Researchers have demonstrated that vehicle armor using composite metal foam (CMF) can stop ball and armor-piercing .50 caliber rounds as well as conventional steel armor, even though it weighs less than half as much. The finding means that vehicle...
A Rutgers-led study sheds light on one of the most enduring mysteries of science: How did metabolism—the process by which life powers itself by converting energy from food into movement and growth—begin?
To answer that question, the researchers reverse-engineered a...
It's a feat three decades in the making: Harvard University chemists have achieved what a new paper calls a "landmark in drug discovery" with the total synthesis of halichondrin. Known to be a potent anti-cancer agent in mouse studies,...
There are many ways to generate electricity—batteries, solar panels, wind turbines, and hydroelectric dams, to name a few examples… and now, there's rust.
New research conducted by scientists at Caltech and Northwestern University shows that thin films of rust—iron oxide—can...
For physicist Percy Zahl, optimizing and preparing a noncontact atomic force microscope (nc-AFM) to directly visualize the chemical structure of a single molecule is a bit like playing a virtual reality video game. The process requires navigating and manipulating...
As recreational marijuana legalization becomes more widespread throughout the U.S., so has concern about what that means for enforcing DUI laws. Unlike a breathalyzer used to detect alcohol, police do not have a device that can be used in...
Though it remains unknown how life began, there is a community of scientists who suspect it occurred in or around deep sea hydrothermal environments. At such sites, water heated by contact with hot rocks from Earth's mantle flows into...
Hypersaline brines—water that contains high concentrations of dissolved salts and whose saline levels are higher than ocean water—are a growing environmental concern around the world. Very challenging and costly to treat, they result from water produced during oil and...
Scientists have developed a large-scale economical method to extract hydrogen (H2) from oil sands (natural bitumen) and oil fields. This can be used to power hydrogen-powered vehicles, which are already marketed in some countries, as well as to generate...
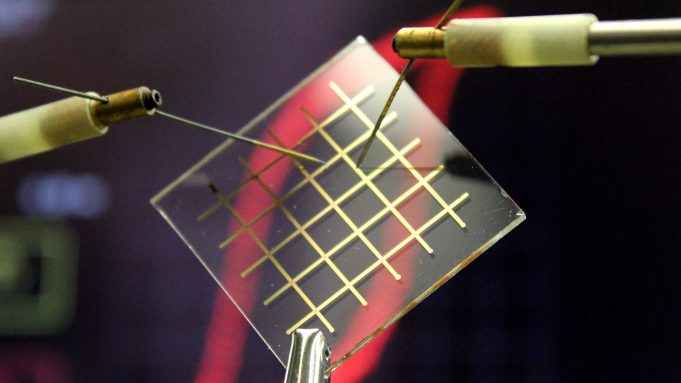
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPI-P) led by Dr. Kamal Asadi have solved a four-decade-long challenge of producing very thin nylon films that can be used in electronic memory components, for instance. The thin nylon...
For 6,000 years, humans have been making things from metal because it's strong and tough; a lot of energy is required to damage it. The flip side of this property is that a lot of energy is required to...