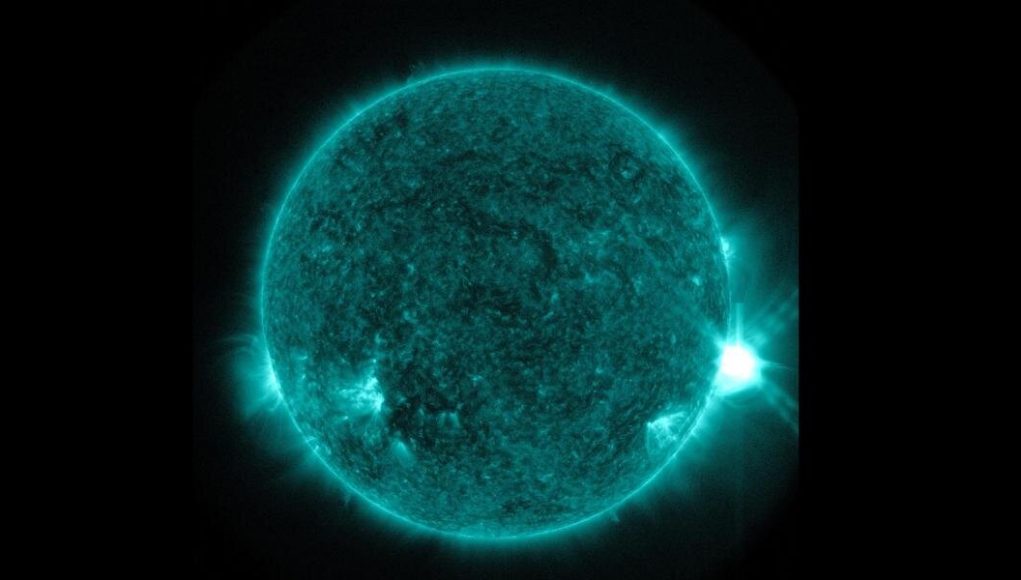
Toward the end of 2017, a massive new region of magnetic field erupted on the Sun’s surface next to an existing sunspot. The powerful collision of magnetic energy produced a series of potent solar flares, causing turbulent space weather conditions at Earth. These were the first flares to be captured, in their moment-by-moment progression, by NJIT’s then recently opened Expanded Owens Valley Solar Array (EOVSA) radio telescope.
In research published in the journal Science, the solar scientists who recorded those images have pinpointed for the first time ever exactly when and where the explosion released the energy that heated spewing plasma to energies equivalent to 1 billion degrees in temperature.
With data collected in the microwave spectrum, they have been able to provide quantitative measurements of the evolving magnetic field strength directly following the flare’s ignition and have tracked its conversion into other energy forms—kinetic, thermal and superthermal—that power the flare’s explosive 5-minute trip through the corona.
To date, these changes in the corona’s magnetic field during a flare or other large-scale eruption have been quantified only indirectly, from extrapolations, for example, of the magnetic field measured at the photosphere—the surface layer of the Sun seen in white light. These extrapolations do not permit precise measurements of the dynamic local changes of the magnetic field in the locations and at time scales short enough to characterize the flare’s energy release.
“We have been able to pinpoint the most critical location of the magnetic energy release in the corona,” said Gregory Fleishman, a distinguished research professor of physics in NJIT’s Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research and author of the paper. “These are the first images that capture the microphysics of a flare—the detailed chain of processes that occur on small spatial and time scales that enable the energy conversion.”
Find your dream job in the space industry. Check our Space Job Board »
By measuring the decline in magnetic energy, and the simultaneous strength of the electric field in the region, they are able to show that the two concord with the law of energy conservation are thus able to quantify the particle acceleration that powers the solar flare, including the associated eruption and plasma heating.
These fundamental processes are the same as those occurring in the most powerful astrophysical sources, including gamma ray bursts, as well as in laboratory experiments of interest to both basic research and the generation of practical fusion energy.
With 13 antennas working together, EOVSA takes pictures at hundreds of frequencies in the 1-18 GHz range, including optical, ultraviolet, X-rays and radio wavelengths, within a second. This enhanced ability to peer into the mechanics of flares opens new pathways to investigate the most powerful eruptions in our solar system, which are ignited by the reconnection of magnetic field lines on the Sun’s surface and powered by stored energy in its corona.
“Microwave emission is the only mechanism that is sensitive to the coronal magnetic field environment, so the unique, high-cadence EOVSA microwave spectral observations are the key to enabling this discovery of rapid changes in the magnetic field,” noted Dale Gary, a distinguished professor of physics at NJIT, EOVSA’s director and a co-author of the paper. “The measurement is possible because the high-energy electrons traveling in the coronal magnetic field dominantly emit their magnetic-sensitive radiation in the microwave range.”
Before EOVSA’s observations, there was no way to see the vast region of space over which high-energy particles are accelerated and then become available for further acceleration by the powerful shock waves driven by the flare eruption, which, if directed at Earth, can destroy spacecraft and endanger astronauts.
“The connection of the flare-accelerated particles to those accelerated by shocks is an important piece in our understanding of which events are benign and which pose a serious threat,” Gary said.
Just over two years after the expanded array began operating, it is automatically generating microwave images of the Sun and making them available to the scientific community on a day-to-day basis. As solar activity increases over the course of the 11-year solar cycle, they will be used to provide the first daily coronal magnetograms, maps of magnetic field strength 1,500 miles above the Sun’s surface.
Provided by New Jersey Institute of Technology
More information: Gregory D. Fleishman et al. Decay of the coronal magnetic field can release sufficient energy to power a solar flare. Science (2020). DOI: 10.1126/science.aax6874
Image Credit: New Jersey Institute of Technology