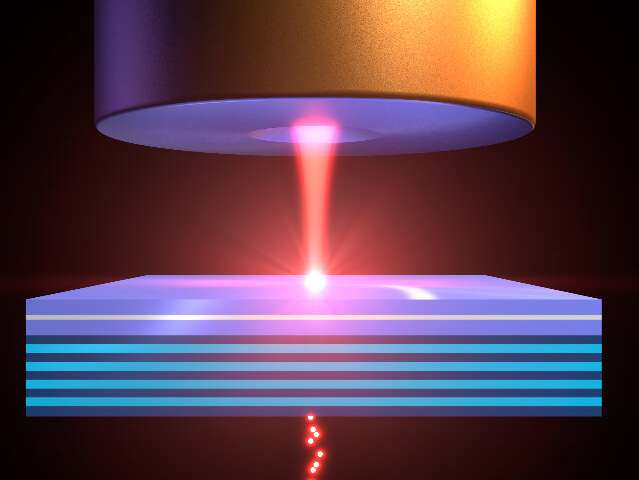
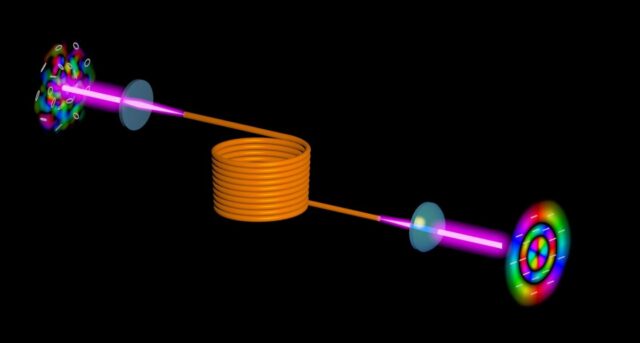
A team of physicists led by Professor Patrick Windpassinger at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has successfully transported light stored in a quantum memory over a distance of 1.2 millimeters. They have demonstrated that the controlled transport process and...
An international team of researchers led out of Macquarie University has demonstrated a new approach for converting ordinary laser light into genuine quantum light.
Their approach uses nanometre-thick films made of gallium arsenide, which is a semiconductor material widely used...
Aalto researchers have used an IBM quantum computer to explore an overlooked area of physics, and have challenged 100-year-old notions about information at the quantum level.
The rules of quantum physics, which govern how very small things behave, use mathematical operators...
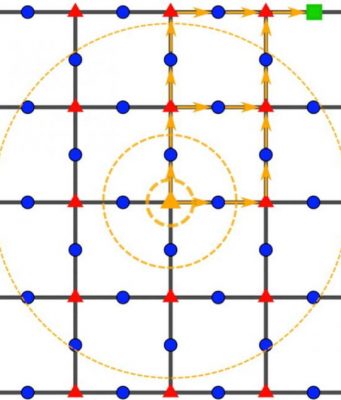
This image shows the basic setup that enables researchers to use lasers as optical "tweezers" to pick individual atoms out from a cloud and hold them in place. The atoms are imaged onto a camera, and the traps are...
Atomic interactions in everyday solids and liquids are so complex that some of these materials' properties continue to elude physicists' understanding. Solving the problems mathematically is beyond the capabilities of modern computers, so scientists at Princeton University have turned...
The use of multimode optical fibers to boost the information capacity of the Internet is severely hampered by distortions that occur during the transmission of images because of a phenomenon called modal crosstalk.
However, University of Rochester researchers at the...
Scientists have calculated the mass range for Dark Matter—and it's tighter than the science world thought.
Their findings—due to be published in Physics Letters B in March—radically narrow the range of potential masses for Dark Matter particles, and help to focus the...
A lens that is a thousand times thinner than a human hair has been developed in Brazil by researchers at the University of São Paulo's São Carlos School of Engineering (EESC-USP). It can serve as a camera lens in...
A new study of airflow patterns inside a car's passenger cabin offers some suggestions for potentially reducing the risk of COVID-19 transmission while sharing rides with others.
The study, by a team of Brown University researchers, used computer models to...
Swansea University scientists working at CERN have published a study detailing a breakthrough in antihydrogen research.
The scientists were working as part of the ALPHA collaboration which is made up of researchers and groups from over a dozen institutions from...
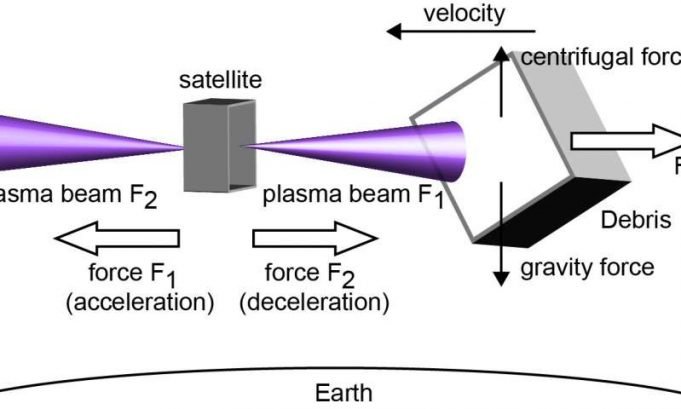
The Earth is currently surrounded by debris launched into space over several decades. This space junk can collide with satellites, causing damage and creating more debris. To preserve a secure space environment, the active removal or de-orbiting of space...