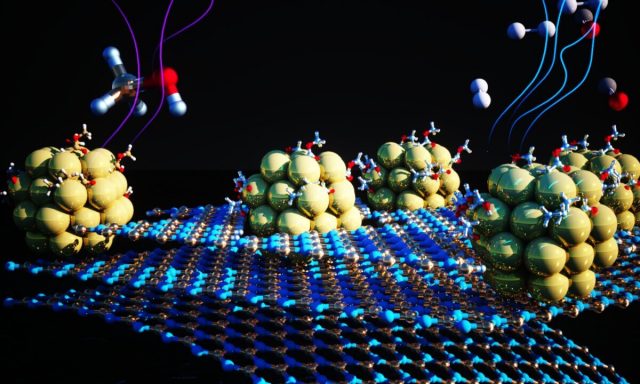
Hydrogen is a sustainable source of clean energy that avoids toxic emissions and can add value to multiple sectors in the economy including transportation, power generation, metals manufacturing, among others. Technologies for storing and transporting hydrogen bridge the gap...
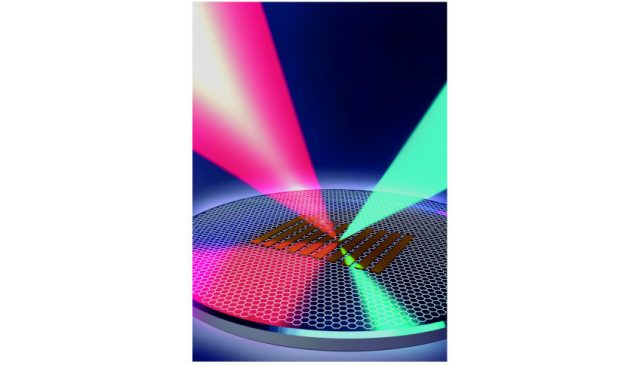
On the electromagnetic spectrum, terahertz light is located between infrared radiation and microwaves. It holds enormous potential for tomorrow's technologies: Among other things, it might succeed 5G by enabling extremely fast mobile communications connections and wireless networks. The bottleneck...
Researchers from the National Graphene Institute at the University of Manchester and the University of Pennsylvania have identified ultra-fast gas flows through the tiniest holes in one-atom-thin membranes, in a study published in Science Advances.
The work—alongside another study from Penn...
In a new study an international research team led by the University of Vienna has shown that structures built around a single layer of graphene allow for strong optical nonlinearities that can convert light. The team achieved this by...
Nanomaterials researchers in Finland, the United States and China have created a color atlas for 466 unique varieties of single-walled carbon nanotubes.
The nanotube color atlas is detailed in a study in Advanced Materials about a new method to predict the specific...
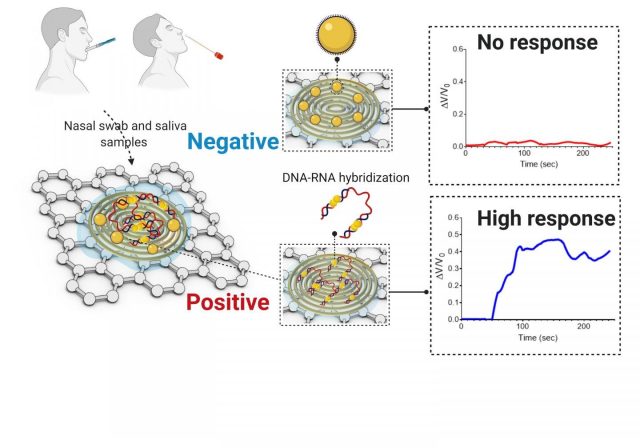
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the world, testing remains a key strategy for tracking and containing the virus. Bioengineering graduate student, Maha Alafeef, has co-developed a rapid, ultrasensitive test using a paper-based electrochemical sensor that can...
Researchers, led by Columbia Engineering Professor Latha Venkataraman, report today that they have discovered a new chemical design principle for exploiting destructive quantum interference. They used their approach to create a six-nanometer single-molecule switch where the on-state current is...
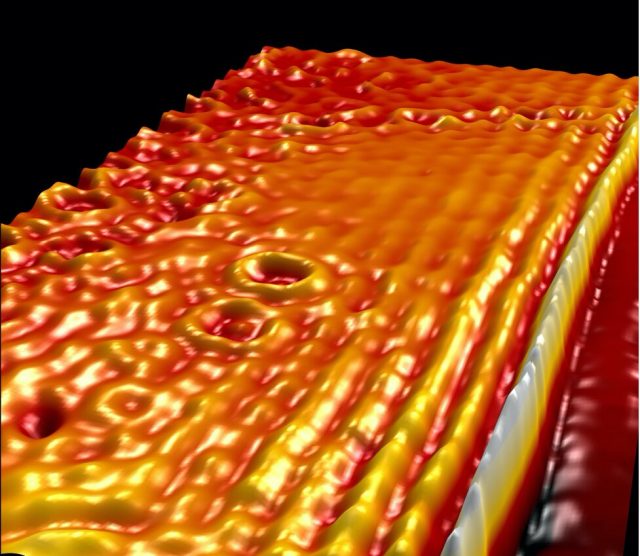
Graphene, an atomically thin carbon layer through which electrons can travel virtually unimpeded, has been extensively studied since its first successful isolation more than 15 years ago. Among its many unique properties is the ability to support highly confined...
Nanoparticles are promising drug delivery tools, offering the ability to administer drugs directly to a specific part of the body and avoid the awful side effects so often seen with chemotherapeutics.
But there's a problem. Nanoparticles struggle to get past...
New research by scientists from Delft University of Technology and the University of Duisburg-Essen uses the motion of atomically thin graphene to identify noble gasses. These gasses are chemically passive and do not react with other materials, which makes...
The quantum sensing abilities of nanodiamonds can be used to improve the sensitivity of paper-based diagnostic tests, potentially allowing for earlier detection of diseases such as HIV, according to a study led by UCL researchers in the i-sense McKendry...