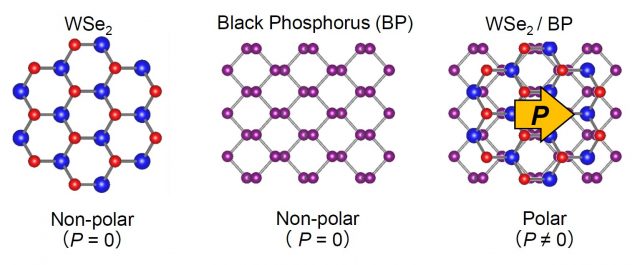
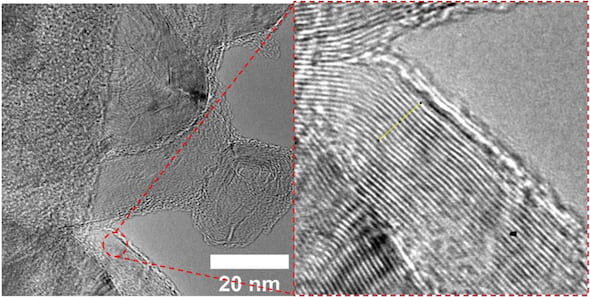
For the first time, researchers have discovered a way to obtain polarity and photovoltaic behavior from certain nonphotovoltaic, atomically flat (2D) materials. The key lies in the special way in which the materials are arranged. The resulting effect is...
The current method of manufacturing carbon nanotubes—in essence rolled up sheets of graphene—is unable to allow complete control over their diameter, length and type. This problem has recently been solved for two of the three different types of nanotubes,...
This could be where the rubber truly hits the road.
Rice University scientists have optimized a process to convert waste from rubber tires into graphene that can, in turn, be used to strengthen concrete.
The environmental benefits of adding graphene to...
Using an ordinary light microscope, MIT engineers have devised a technique for imaging biological samples with accuracy at the scale of 10 nanometers—which should enable them to image viruses and potentially even single biomolecules, the researchers say.
The new technique...
Scientists have developed a method to use lasers to control the movement of nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers.
Scientists have long been working on improving their ability to use lasers to move small objects without actually touching them. This method of...
Scientists make pivotal discovery of method for wireless modulation of neurons with X-rays that could improve the lives of patients with brain disorders. The X-ray source only requires a machine like that found in a dentist's office.
Many people worldwide...
2D materials have triggered a boom in materials research. Now it turns out that exciting effects occur when two such layered materials are stacked and slightly twisted.
The discovery of the material graphene, which consists of only one layer of...
Training neural networks to perform tasks, such as recognizing images or navigating self-driving cars, could one day require less computing power and hardware thanks to a new artificial neuron device developed by researchers at the University of California San...
Quantum dots are manmade nanoparticles of semiconducting material comprising only a few thousand atoms. Because of the small number of atoms, a quantum dot's properties lie between those of single atoms or molecules and bulk material with a huge...
Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new method for making ordered arrays of nanoholes in metallic oxide thin films using a range of transition metals. The team used a template to pre-pattern metallic surfaces with an ordered...
The recent synthesis of one-dimensional van der Waals heterostructures, a type of heterostructure made by layering two-dimensional materials that are one atom thick, may lead to new, miniaturized electronics that are currently not possible, according to a team of...