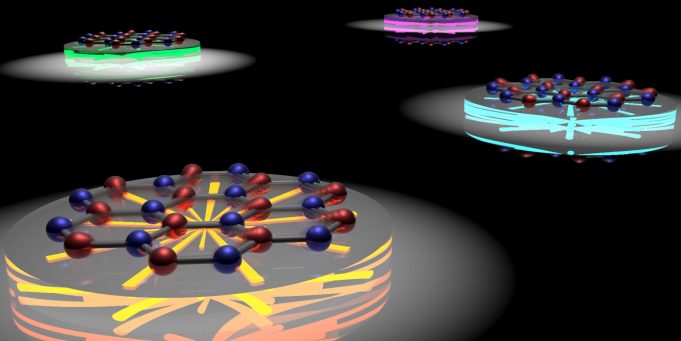
Wavelike, collective oscillations of electrons known as "plasmons" are very important for determining the optical and electronic properties of metals.
In atomically thin 2-D materials, plasmons have an energy that is more useful for applications, including sensors and communication devices,...
Writing in the journal NanoResearch, a team at the University of Massachusetts Amherst reports this week that they have developed bioelectronic ammonia gas sensors that are among the most sensitive ever made.
The sensor uses electric-charge-conducting protein nanowires derived from the bacterium...
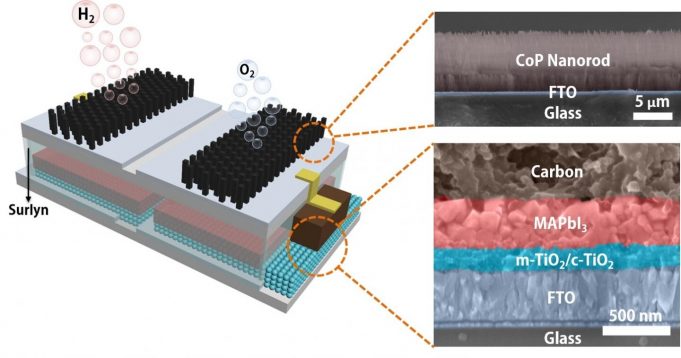
Rice University researchers have created an efficient, low-cost device that splits water to produce hydrogen fuel.
The platform developed by the Brown School of Engineering lab of Rice materials scientist Jun Lou integrates catalytic electrodes and perovskite solar cells that, when triggered...
In regenerative medicine, an ideal treatment for patients whose muscles are damaged from lack of oxygen would be to invigorate them with an injection of their own stem cells.
In a new study published in the journal ACS Nano, researchers at...
In the study, published in the journal Physical Review B, the researchers showed that bilayer graphene, consisting of two layers of graphene, was noticeably softer than both two-dimensional (2-D) graphene and three-dimensional (3-D) graphite along the stacking direction.
This surprising result...
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that people wear masks in public. Because N95 and surgical masks are scarce and should be reserved for health care workers, many people...
As electronic devices become progressively smaller, the technology that powers them needs to get smaller and thinner.
One of the key challenges scientists face in developing this technology is finding materials that can perform well at an ultrathin size. But...
A team of biomaterials scientists and dentists at the UCLA School of Dentistry has developed a nanoparticle that, based on initial experiments in animals, could improve treatment for bone defects.
A paper describing the advance is published today in the...
Only 10 years ago, scientists working on what they hoped would open a new frontier of neuromorphic computing could only dream of a device using miniature tools called memristors that would function/operate like real brain synapses.
But now a team...
MIT engineers have developed a way to closely track how plants respond to stresses such as injury, infection, and light damage, using sensors made of carbon nanotubes. These sensors can be embedded in plant leaves, where they report on...
A team of Australian scientists from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) and the Australian National University (ANU) believe they have developed a way to address a decades-long challenge in the field of quantum materials—the spectral tuning of proposed...