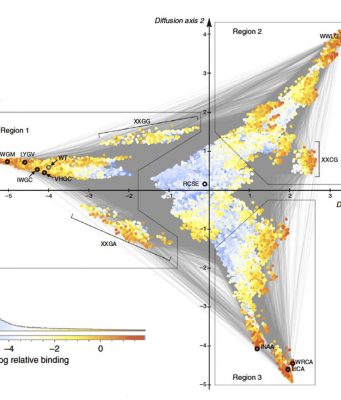
Some patients with breast cancer receive chemotherapy before the tumor is removed with surgery. This approach, called neoadjuvant therapy, helps to reduce the size of the tumor to facilitate breast-conserving surgery, and can even eradicate the tumor, leaving few...
Fever is known to help power up our immune cells, and scientists in Shanghai have new evidence explaining how. They found in mice that fever alters surface proteins on immune cells like lymphocytes to make them better able to...
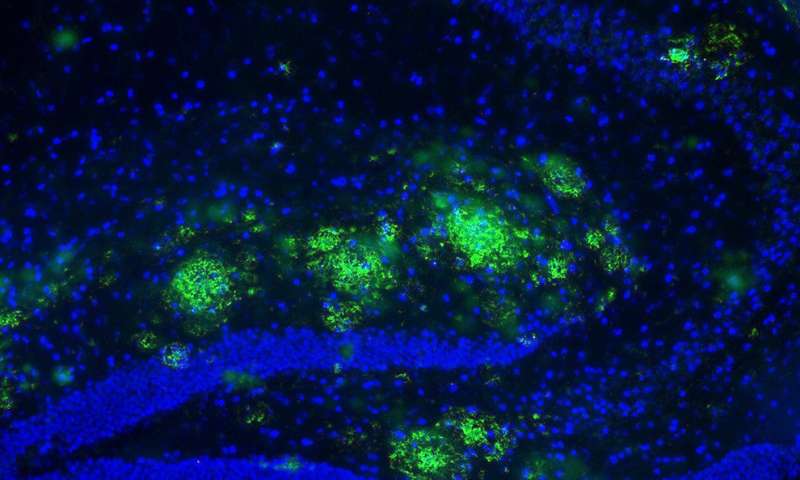
Research published today (Jan. 22) in the journal Brain reveals a new approach to Alzheimer's disease (AD) that may eventually make it possible to reverse memory loss, a hallmark of the disease in its late stages.
The team, led by...
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a new imaging agent that could let doctors identify not only multiple types of tumors but the surrounding normal cells that the cancer takes over and uses...
Regular use of a common type of medication, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, significantly improves survival for a third or more patients with head and neck cancer, a new study led by UC San Francisco has found.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,...
A fungus that attacks almond and peach trees may be key to identifying new drug targets for cancer therapy.
A team of Florida State University researchers from the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry found that a natural product from the...
When it comes to inpatient treatment of a range of mental health and mood disorders -- from anxiety and depression to schizophrenia, suicidality and acute psychotic episodes -- a new study advocates for exercise, rather than psychotropic medications, as...
Chemotherapy and radiation are effective cancer treatments because they kill rapidly dividing cells, including tumor cells. But for children—whose tiny bodies are still growing—these treatments can cause lifelong damage. This is particularly true for children with brain cancer, and...
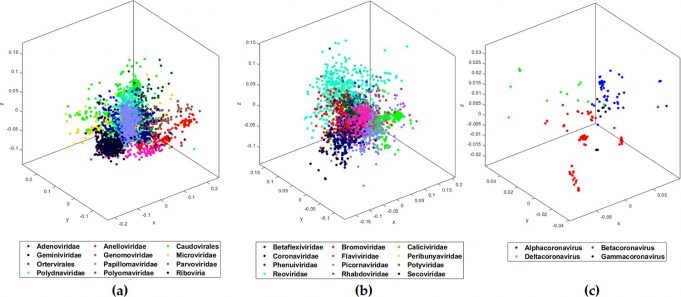
Using machine learning, a team of Western computer scientists and biologists have identified an underlying genomic signature for 29 different COVID-19 DNA sequences.
This new data discovery tool will allow researchers to quickly and easily classify a deadly virus like...
Yale researchers have identified a drinkable cocktail of designer molecules that interferes with a crucial first step of Alzheimer's and even restores memories in mice, they report Jan. 2 in the journal Cell Reports.
The binding of amyloid beta peptides...
Chaos in bodily regulation can optimize our immune system according to a recent discovery made by researchers at the University of Copenhagen's Niels Bohr Institute. The discovery may prove to be of great significance for avoiding serious diseases such...