A new federal rule that determines how the Clean Water Act is implemented leaves millions of miles of streams and acres of wetlands unprotected based on selective interpretation of case law and a distortion of scientific evidence, researchers say...
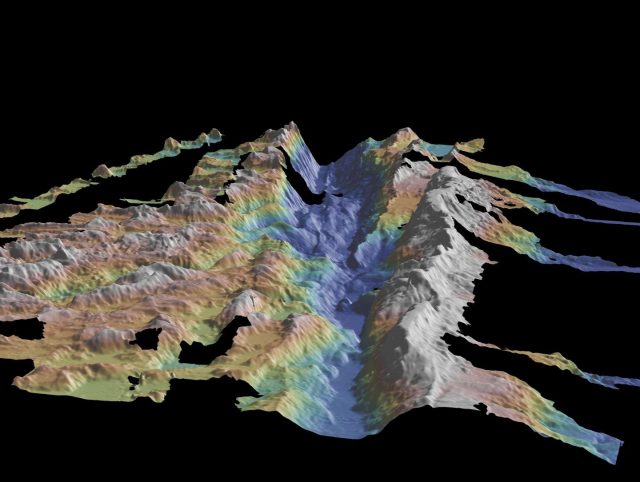
A synthesis of volcanic vents on the surface and data that probes the structure and composition of the crust to a depth of 20 kilometers (12.4 miles) makes clear new connections between surface and subsurface evidence of past volcanic eruptions....
Scientists have tracked a 'boomerang' earthquake in the ocean for the first time, providing clues about how they could cause devastation on land.
Earthquakes occur when rocks suddenly break on a fault—a boundary between two blocks or plates. During large earthquakes, the...
Plastic from used personal protective equipment (PPE) can, and should, be transformed into renewable liquid fuels—according to a new study, published in the peer-reviewed Taylor & Francis journal Biofuels.
Experts from The University of Petroleum and Energy Studies have suggested a...
Clean-up devices that collect waste from the ocean surface won't solve the plastic pollution problem, a new study shows.
Researchers compared estimates of current and future plastic waste with the ability of floating clean-up devices to collect it—and found the impact of...
A majority of the world population lives on low lying lands near the sea, some of which are predicted to submerge by the end of the 21st century due to rising sea levels.
The most relevant quantity for assessing the...
An international team discovered a previously unrecognized ocean current that transports water to one of the world's largest "waterfalls" in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Bank Channel Overflow into the deep North Atlantic. While investigating the pathways that...
At least twice in Earth's history, nearly the entire planet was encased in a sheet of snow and ice. These dramatic "Snowball Earth" events occurred in quick succession, somewhere around 700 million years ago, and evidence suggests that the...
Plato, the Greek philosopher who lived in the 5th century B.C.E., believed that the universe was made of five types of matter: earth, air, fire, water, and cosmos. Each was described with a particular geometry, a platonic shape. For...
Weather forecasts have become less accurate during the COVID-19 pandemic due to the reduction in commercial flights, according to new research.
A new study in AGU's journal Geophysical Research Letters finds the world lost 50-75% of its aircraft weather observations between March...
A newly identified fault system in southeastern Nepal has the potential to cause earthquakes in a densely populated area, according to two University of Alberta scientists who were part of an international team that made the discovery.
"We discovered a...