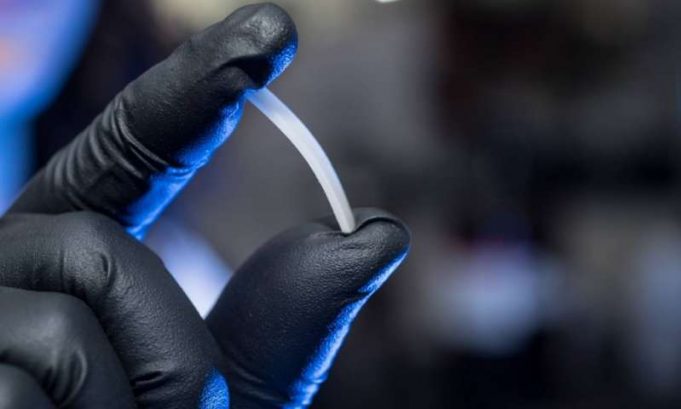
Purdue engineers have figured out a way to tackle plastic landfills while also improving batteries – by putting ink-free plastic soaked in sulfur-containing solvent into a microwave, and then into batteries as a carbon scaffold.
Lithium-sulfur batteries have been hailed...
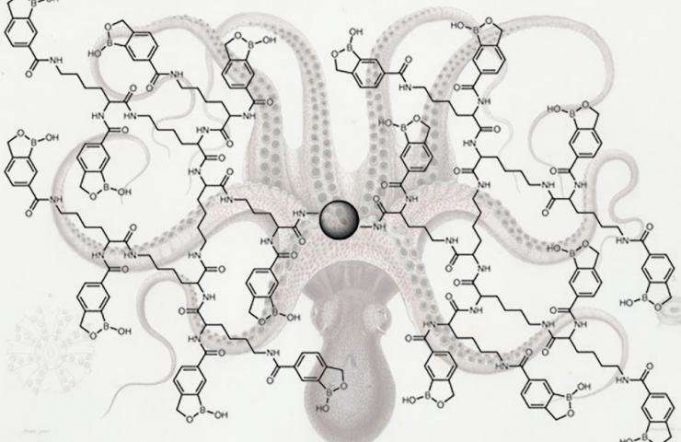
Cancer drops sparse chemical hints of its presence early on, but unfortunately, many of them are in a class of biochemicals that could not be detected thoroughly, until now.
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have engineered a chemical...
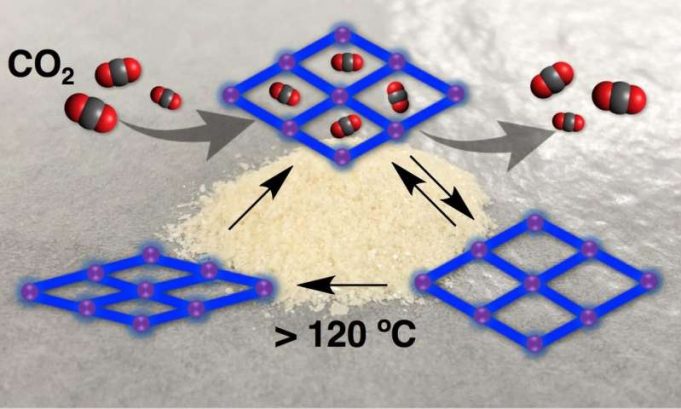
A new, stable artificial photosynthesis device doubles the efficiency of harnessing sunlight to break apart both fresh and salt water, generating hydrogen that can then be used in fuel cells.
The device could also be reconfigured to turn carbon dioxide...
Public water quality has received a lot of attention in recent years as some disturbing discoveries have been made regarding lead levels in cities across the country. Now, a new study from the Johns Hopkins University pinpoints other chemicals...
When the body detects a threat, be it a viral invader or an Alzheimer's disease plaque, guardian proteins on the cell surface kick into gear.
The proteins, called gasdermins, set off a cascade of responses that induce cell death and...
Kyoto University scientists are one step closer to designing porous materials that can change and retain their shapes—a function known as shape-memory effect.
Shape-memory materials have applications in many fields. For example, they could be implanted in the body and...
In a new study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry (JBC), researchers from the University of Notre Dame and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have found that the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a pathogen that causes pneumonia, sepsis...
The world fell in love with plastics because they're cheap, convenient, lightweight and long- lasting. For these same reasons, plastics are now trashing the Earth.
Colorado State University chemists have announced in the journal Science another major step toward waste-free,...
A team of international scientists have created a new form of highly-efficient, low-cost insulation based on the wings of a dragonfly.
The material, known as an aerogel, is the most porous material known to man and ultralight, with a piece...
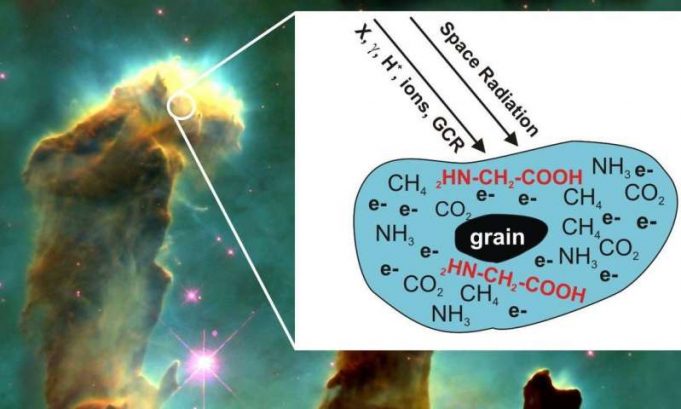
In a laboratory experiment that mimics astrophysical conditions, with cryogenic temperatures in an ultrahigh vacuum, scientists used an electron gun to irradiate thin sheets of ice covered in basic molecules of methane, ammonia and carbon dioxide. These simple molecules...
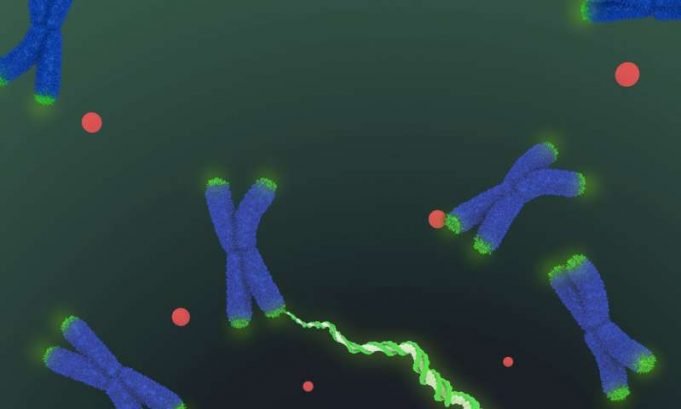
More than 30 years ago, when University of California, Berkeley researchers discovered telomerase—an enzyme that lengthens chromosome ends and prevents them from fraying enough to kill a cell—speculation ran wild about its role in aging and cancer, setting off...