Notorious asphyxiator carbon monoxide has few true admirers, but it's favored by University of California, Irvine scientists who use it to study other molecules.
With the aid of a scanning tunneling microscope, researchers in UCI's Center for Chemistry at the...
Infections with Salmonella bacteria, often caused by eating or handling undercooked meat or eggs, affect about 100 million people a year worldwide. The suffering the infection causes—abdominal cramps, fever and diarrhea—is the result of an extremely precise set of...
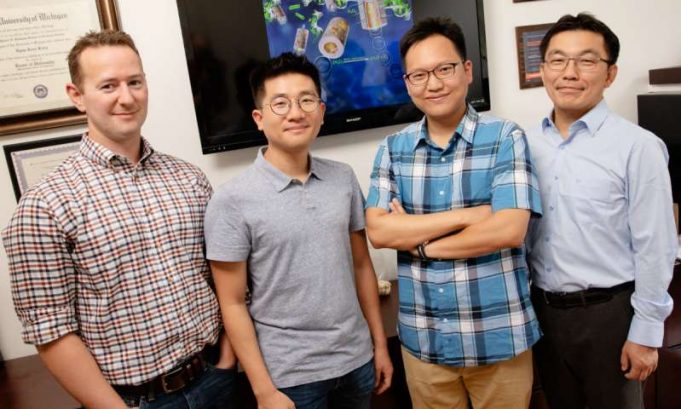
A new type of battery developed by researchers at MIT could be made partly from carbon dioxide captured from power plants. Rather than attempting to convert carbon dioxide to specialized chemicals using metal catalysts, which is currently highly challenging,...
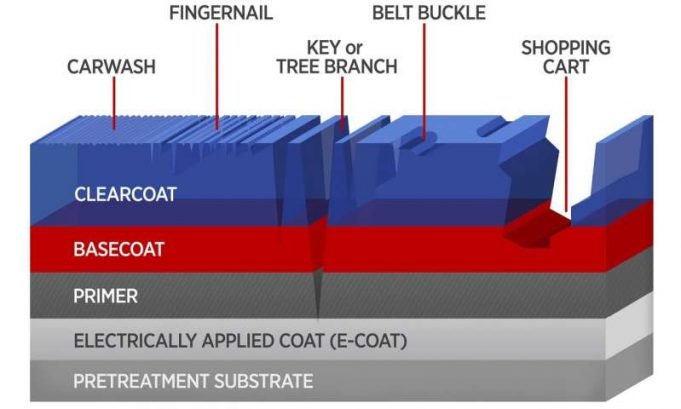
Know that sickening feeling when you exit the grocery store and find your car has been banged up by a runaway shopping cart? It may one day be just a bad memory if auto body manufacturers make use of...
Stiff microbial films often coat medical devices, household items and infrastructure such as the inside of water supply pipes, and can lead to dangerous infections. Researchers have developed a system that harnesses the power of bubbles to propel tiny...
When it comes to designing and optimizing mechanical systems, scientists understand the physical laws surrounding them well enough to create computer models that can predict their properties and behavior. However, scientists who are working to design better electrochemical systems,...
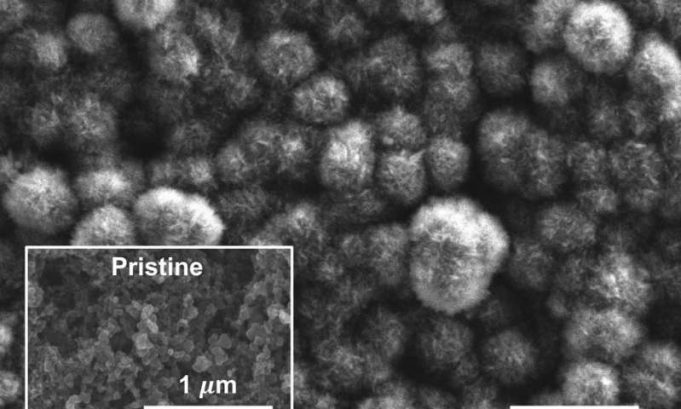
Over the past three decades, lithium-ion batteries, rechargeable batteries that move lithium ions back and forth to charge and discharge, have enabled smaller devices that juice up faster and last longer.
Now, X-ray experiments at the Department of Energy's SLAC...
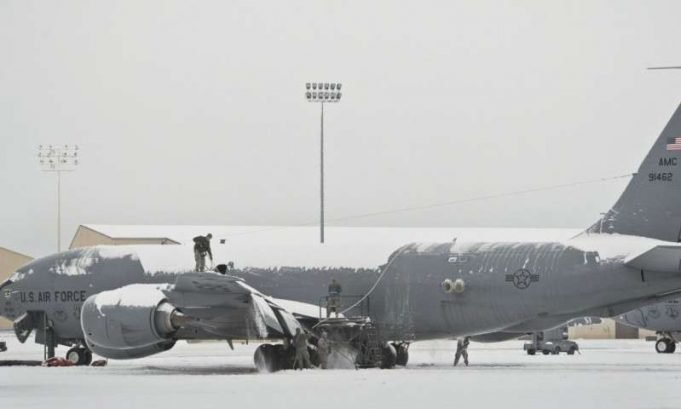
Nothing foretells the coming of winter like frost on windshields.
While the inconvenience of scraping or defrosting car windows may define cold mornings for many drivers, the toll frost takes on the larger economy is more than just a nuisance....
Using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, Columbia Engineers are first to observe how CO2 is activated at the electrode-electrolyte interface; their finding shifts the catalyst design from trial-and-error paradigm to a rational approach and could lead to alternative, cheaper, and safer...
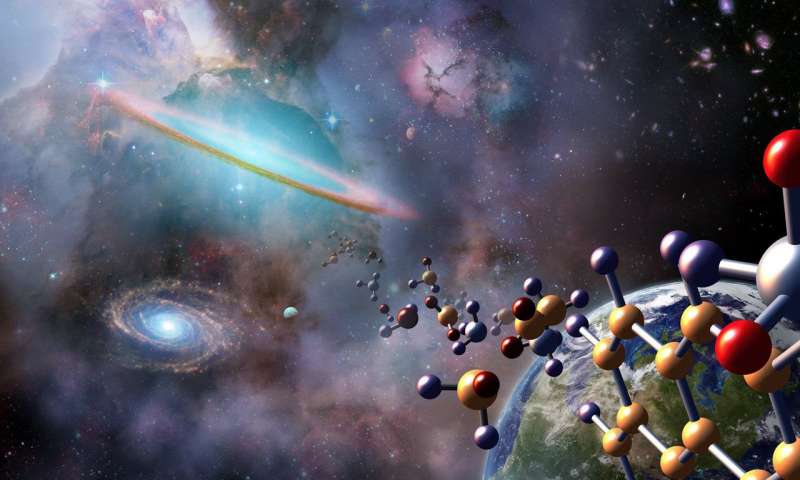
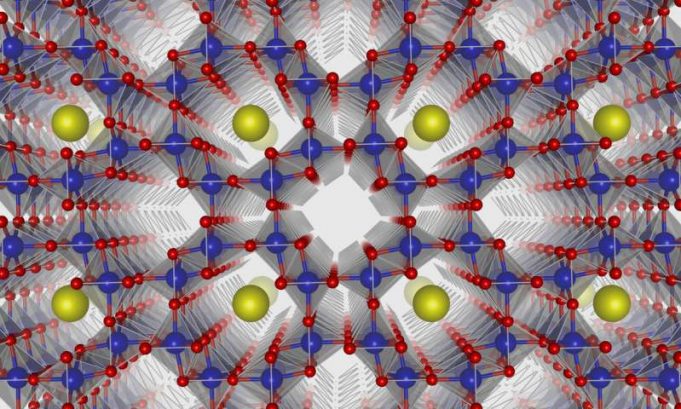
Researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology may have made headway in helping determine the origin of life by identifying three different molecules that self-assemble to form a molecular structure with features characteristic of modern RNA.
RNA – or ribonucleic...
Researchers have cleared one hurdle toward environmental cleanup of certain contaminants with a newly designed synthetic enzyme that reduces the compound sulfite to sulfide—a notoriously complex multistep chemical reaction that has eluded chemists for years.
In the journal Science, chemists...