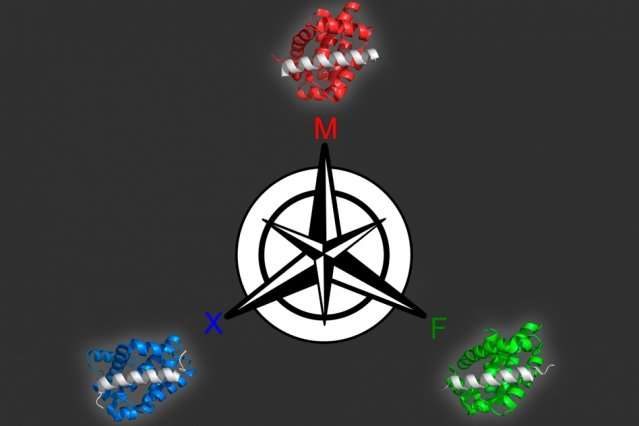
Designing synthetic proteins that can act as drugs for cancer or other diseases can be a tedious process: It generally involves creating a library of millions of proteins, then screening the library to find proteins that bind the correct...
Biomedical engineers from Duke University and Washington University in St. Louis have demonstrated that, by injecting an artificial protein made from a solution of ordered and disordered segments, a solid scaffold forms in response to body heat, and in...
World energy consumption projections predict that coal will remain one of the world's main energy sources in coming decades, and a growing share of it will be used in CTL, the conversion of coal to liquid fuels. Researchers from...
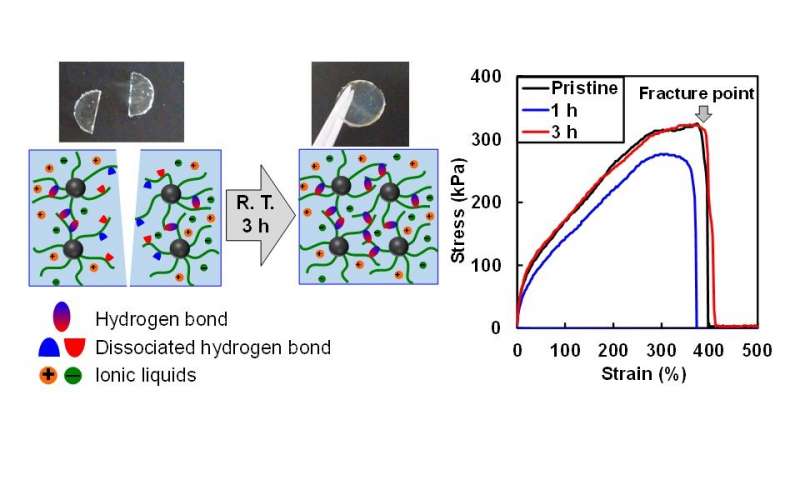
Scientists at Yokohama National University and the University of Tokyo in Japan have designed an ion gel with excellent toughness and an ability to self-heal at ambient temperature without any external trigger or detectable change in the environment such...
Chemists at The Ohio State University have developed a new and improved way to generate molecules that can enable the design of new types of synthetic drugs.
Researchers say this new method of forming reactive intermediates called ketyl radicals offers...
University of Michigan researchers have developed a powerful microscope that can map how light energy migrates in photosynthetic bacteria on timescales of one-quadrillionth of a second.
The microscope could help researchers develop more efficient organic photovoltaic materials, a type of...
The cost of making plastics, paints, coatings for cell phone screens and other materials that heal themselves like skin could be dramatically reduced thanks to a breakthrough that a Clemson University team detailed in the latest edition of the...
A material designed by MIT chemical engineers can react with carbon dioxide from the air, to grow, strengthen, and even repair itself. The polymer, which might someday be used as construction or repair material or for protective coatings, continuously...
How life arose from non-living chemicals more than 3.5 billion years ago on Earth is a still-unanswered question. The RNA world hypothesis assumes that RNA biomolecules were key players during this time as they carry genetic information and act...
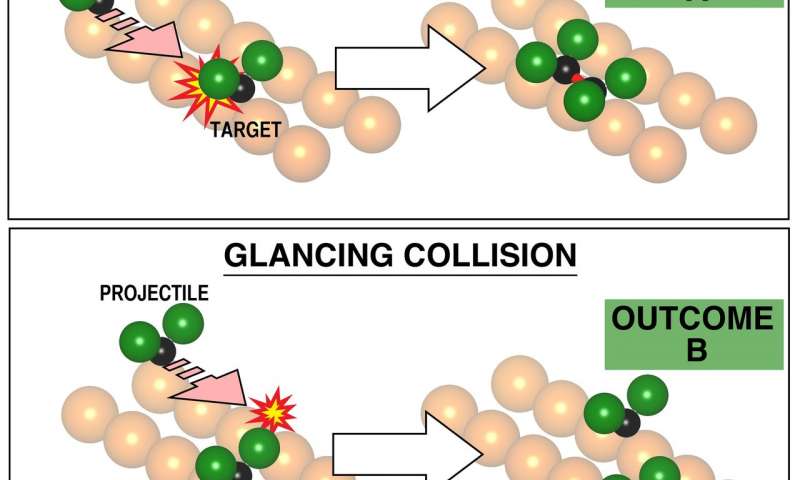
Scientists at the University of Toronto have found a way to select the outcome of chemical reaction by employing an elusive and long-sought factor known as the 'impact parameter'.
The team of U of T chemists, led by Nobel Prize-winning...
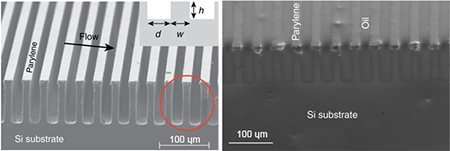
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a super-hydrophobic surface that can be used to generate electrical voltage. When salt water flows over this specially patterned surface, it can produce at least 50 millivolts. The proof-of-concept...