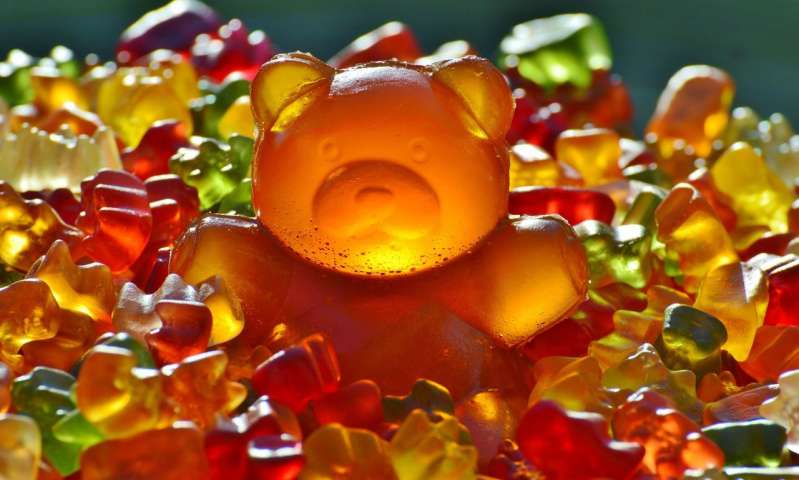
Today, sugar has a villainous reputation. And while too much of the sweet stuff should be avoided, all living things need sugar to survive. "The biological universe is coated with sugars," said Samuel M. Levi and Qiuhan Li, graduate...
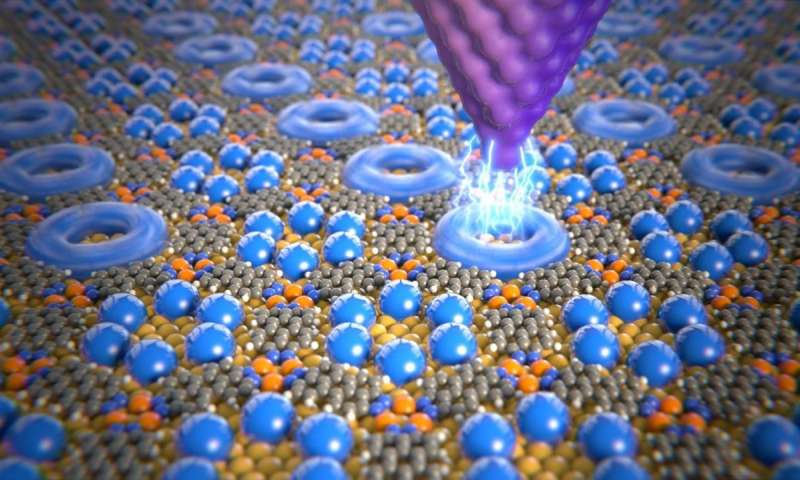
Researchers from the University of Basel have reported a new method that allows the physical state of just a few atoms or molecules within a network to be controlled. It is based on the spontaneous self-organization of molecules into...
The venom of insects such as wasps and bees is full of compounds that can kill bacteria. Unfortunately, many of these compounds are also toxic for humans, making it impossible to use them as antibiotic drugs.
After performing a systematic...
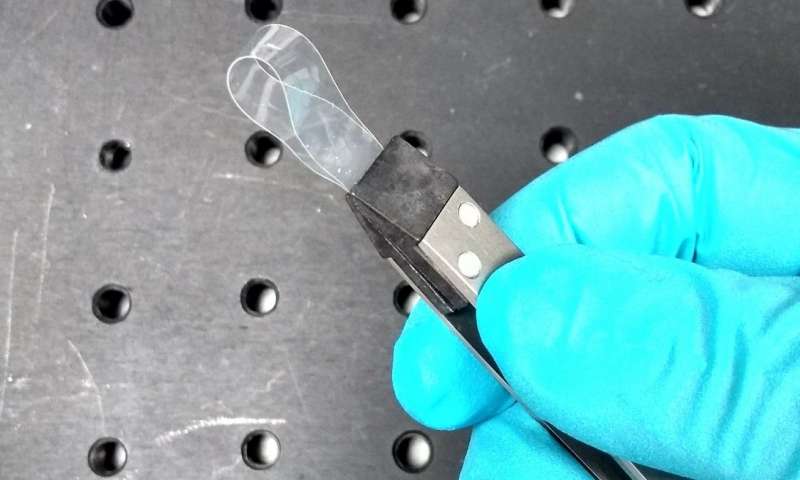
From iPhones on Earth to rovers on Mars, most electronics only function within a certain temperature range. By blending two organic materials together, researchers at Purdue University could create electronics that withstand extreme heat.
This new plastic material could reliably...
A team of materials scientists from Penn State, Cornell and Argonne National Laboratory have, for the first time, visualized the 3-D atomic and electron density structure of the most complex perovskite crystal structure system decoded to date.
Perovskites are minerals...
Plants rely on the energy in sunlight to produce the nutrients they need. But sometimes they absorb more energy than they can use, and that excess can damage critical proteins. To protect themselves, they convert the excess energy into...
Scientists have discovered the first synthetic material that becomes thicker—at the molecular level—as it is stretched.
Researchers led by Dr. Devesh Mistry from the University of Leeds discovered a new non-porous material that has unique and inherent "auxetic" stretching properties....
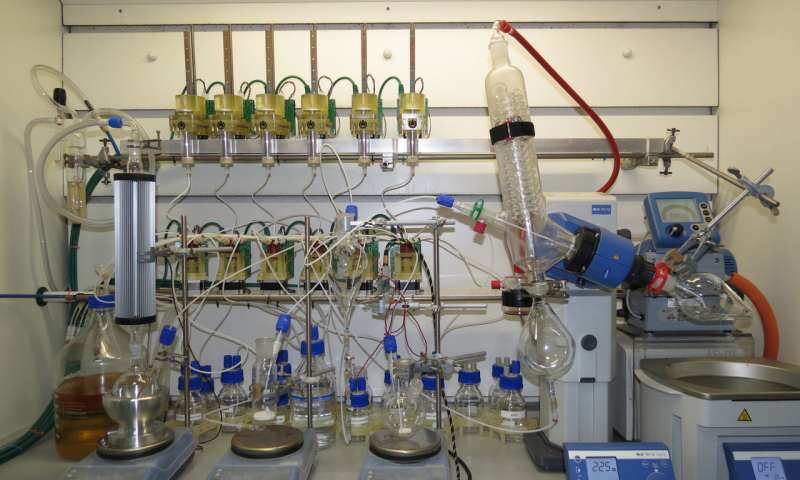
A radical new method of producing drug molecules, which uses downloadable blueprints to easily and reliably synthesise organic chemicals via a programmable 'chemputer', could be set to democratise the pharmaceutical industry, scientists say.
In a new paper published online in...
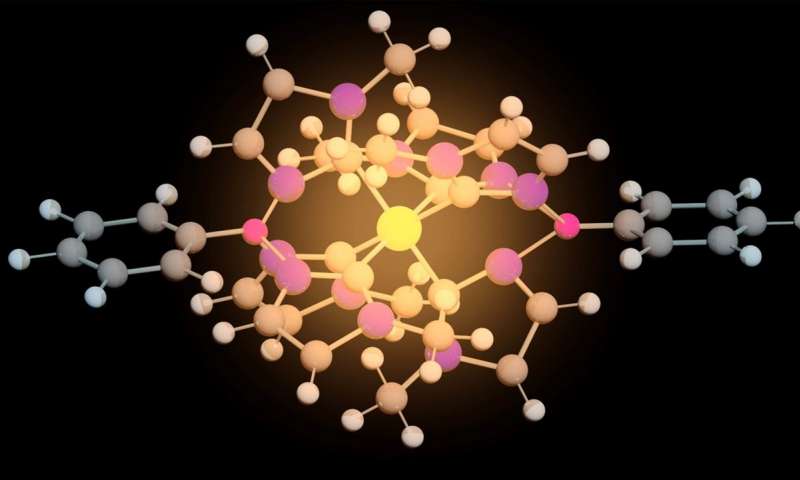
For the first time, researchers have succeeded in creating an iron molecule that can function both as a photocatalyst to produce fuel and in solar cells to produce electricity. The results indicate that the iron molecule could replace the...
QUT chemistry researchers have discovered cheaper and more efficient materials for producing hydrogen for the storage of renewable energy that could replace current water-splitting catalysts.
Professor Anthony O'Mullane said the potential for the chemical storage of renewable energy in the...
Russian scientists with colleagues from the U.K., Spain, Brazil, Japan and Austria have fully described the mechanism of fungal luminescence. They report that fungi utilize only four key enzymes to produce light and that transfer of these enzymes into...