Materials are widely used to help heal wounds: Collagen sponges help treat burns and pressure sores, and scaffold-like implants are used to repair bones. However, the process of tissue repair changes over time, so scientists are developing biomaterials that...
Messenger RNA, which can induce cells to produce therapeutic proteins, holds great promise for treating a variety of diseases. The biggest obstacle to this approach so far has been finding safe and efficient ways to deliver mRNA molecules to...
The idea of using hydrogen as the basis of a clean sustainable energy source, often termed a hydrogen economy, has been a topic of conversation for decades. Hydrogen fuel, for example, doesn't emit any carbon dioxide and is considered...
New developments in antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) with antibiofilm properties are rapidly materializing. ABP works by inhibiting antibiotic resistant bacteria in the biofilm through nucleotide signaling molecules.
Antimicrobial peptides and antibiofilm peptide (ABP) are new antibiotic molecules derived from microorganisms for...
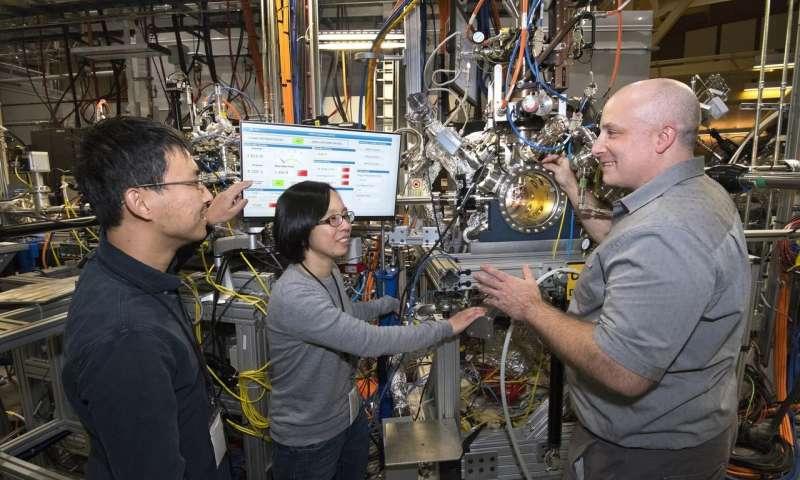
Imagine trying to figure out how something works when that something takes place in a space smaller than a femtoliter: one quadrillionith of a liter. Now, two scientists with a nose for solving mysteries have used a combination of...
By enticing away the repressors dampening unexpressed, silent genes in Streptomyces bacteria, researchers at the University of Illinois have unlocked several large gene clusters for new natural products, according to a study published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology.
Since...
Humans can get by in the most basic of shelters, can scratch together a meal from the most humble of ingredients. But we can't survive without clean water. And in places where water is scarce—the world's deserts, for example—getting...
Hydrogen fuel cells are a promising technology for producing clean and renewable energy, but the cost and activity of their cathode materials is a major challenge for commercialization. Many fuel cells require expensive platinum-based catalysts—substances that initiate and speed...
As a non-noble metal, copper oxidizes more easily to a positive valence (Cu+ or Cu2+) than same-family elements Au or Ag. In general, this chemical property is mainly determined by electron structure. Can we change the chemical properties of...
Scientists at Stanford University have designed an electrocatalytic mechanism that works like a mammalian lung to convert water into fuel. Their research, published December 20 in the journal Joule, could help existing clean energy technologies run more efficiently.
The act...
MIT researchers have demonstrated a new way to store unused heat from car engines, industrial machinery, and even sunshine until it's needed. Central to their system is what the researchers refer to as a "phase-change" material that absorbs a...