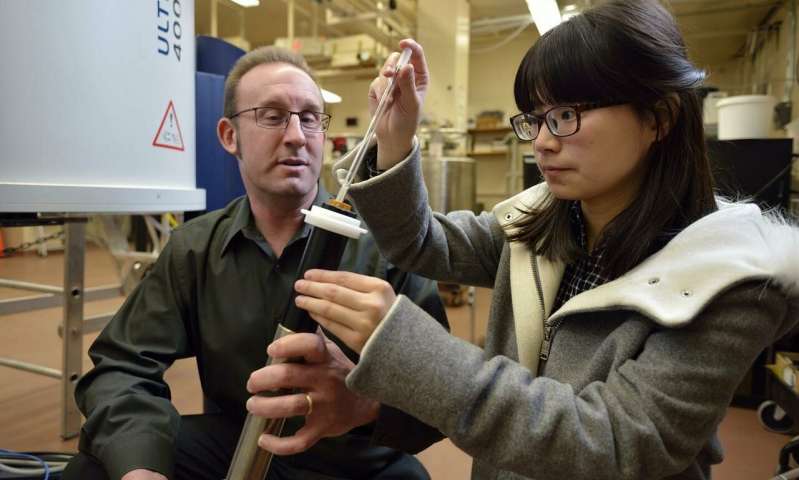
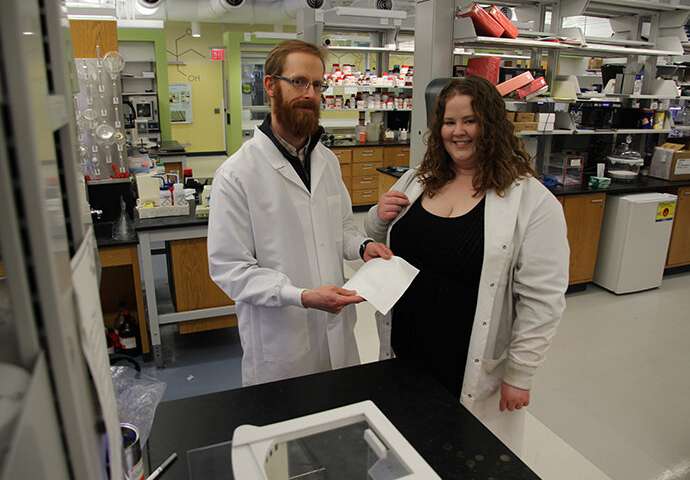
A team of scientists including researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have identified the causes of degradation in a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries, as well as possible remedies....
One of the greatest global challenges is the efficient use of renewable sources in order to meet the increasing demand for energy and feedstock chemicals in the future. In this context, biomass is a promising alternative to existing fossil...
Trihydrogen, or H3+, is acknowledged by scientists as the molecule that made the universe. In recent issues of Nature Communications and the Journal of Chemical Physics, Michigan State University researchers employed high-speed lasers to shine a spotlight on the mechanisms that are...
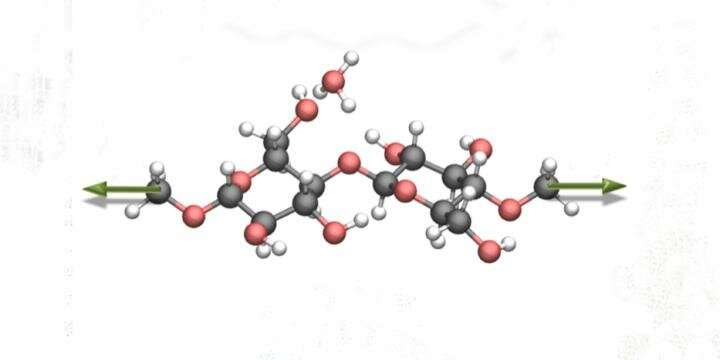
Researchers in the College of Science and College of Engineering have discovered that a high-strength polymer called "PBDT" has a rare double helix structure, opening possibilities for use in a variety of applications.
This discovery, recently published in Nature Communications, comes...
Scientists have found a new way to control light emitted by exotic crystal semiconductors, which could lead to more efficient solar cells and other advances in electronics, according to a Rutgers-led study in the journal Materials Today.
Their discovery involves crystals...
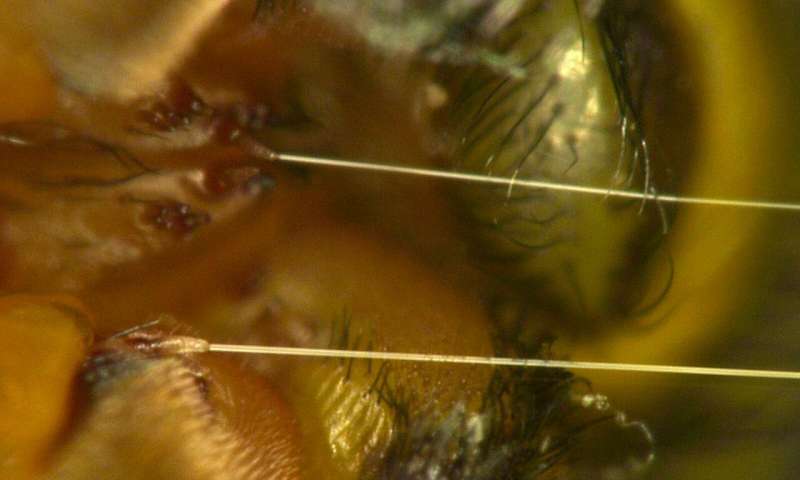
Spider silk, already known as one of the strongest materials for its weight, turns out to have another unusual property that might lead to new kinds of artificial muscles or robotic actuators, researchers have found.
The resilient fibers, the team...
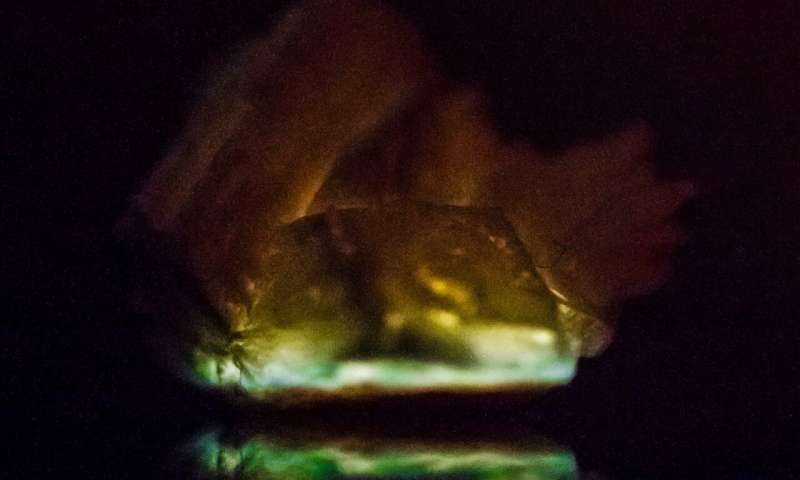
The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, demonstrate that this fundamental process of transduction of energy—heat, applied to a material, generates light—can be achieved in pure solid materials of millimeter or centimeter size.
In general, chemiluminescence reactions are only...
Electricity can be generated by renewable sources such as sunlight and wind, then used to split water, which makes hydrogen as a fuel for emerging energy devices such as fuel cells. Because hydrogen is a clean fuel, researchers are...
Researchers have used liquid metals to turn carbon dioxide back into solid coal, in a world-first breakthrough that could transform our approach to carbon capture and storage.
The research team led by RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, have developed...
Researchers in the College of Engineering and Computer Science have developed a material—a new kind of shape memory polymer (SMP)—that could have major implications for health care.
SMPs are soft, rubbery, "smart" materials that can change shape in response to...
Researchers have found that liquid has structure in certain circumstances, and that this structure significantly influences the mysterious and complex formation of metallic glasses.
Moldable like plastic but strong like metal, metallic glasses are a relatively new class of materials...