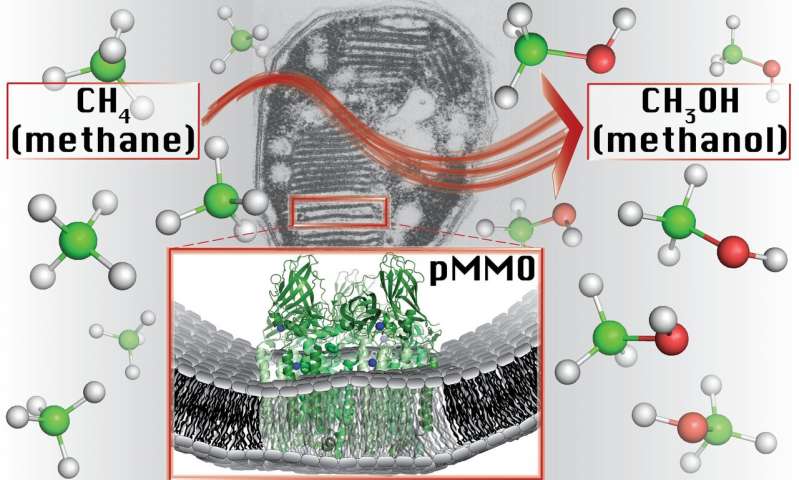
Known for their ability to remove methane from the environment and convert it into a usable fuel, methanotrophic bacteria have long fascinated researchers. But how, exactly, these bacteria naturally perform such a complex reaction has been a mystery.
Now an...
Washington State University researchers have developed an environmentally-friendly, plant-based material that for the first time works better than Styrofoam for insulation.
The foam is mostly made from nanocrystals of cellulose, the most abundant plant material on earth. The researchers also developed an...
A cheaper, cleaner and more sustainable way of making hydrogen fuel from water using sunlight is step closer thanks to new research from the University of Bath's Centre for Sustainable Chemical Technologies.
With the pressure on global leaders to reduce carbon emissions significantly to...
Hypersaline brines—water that contains high concentrations of dissolved salts and whose saline levels are higher than ocean water—are a growing environmental concern around the world. Very challenging and costly to treat, they result from water produced during oil and...
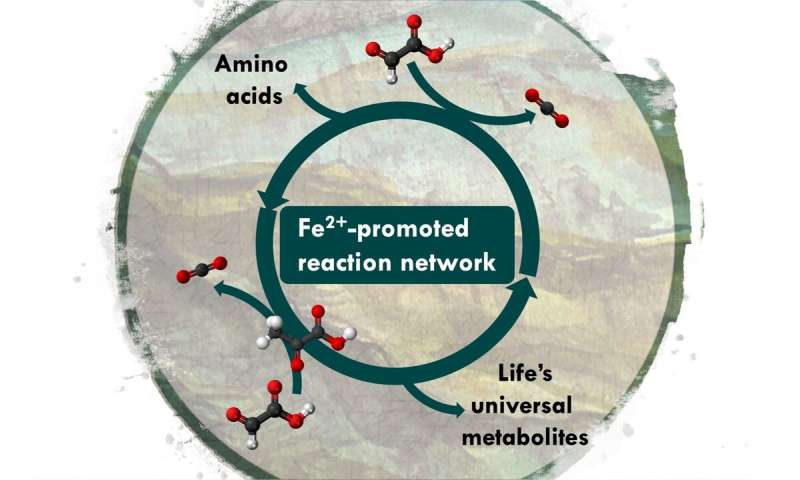
Researchers in Strasbourg, France, have found that mixing two small biomolecules, glyoxylate and pyruvate, in iron-salt-rich water produces a reaction network resembling life's core biochemistry. This discovery provides insight into how chemistry on the early Earth primed the evolution...
York University chemists have invented a new fluorescence-based method for accurately determining the strength of a range of Lewis acids, which could one day be used to help purify pharmaceutical drugs, improve industrial processes and explore next-generation technologies, according...
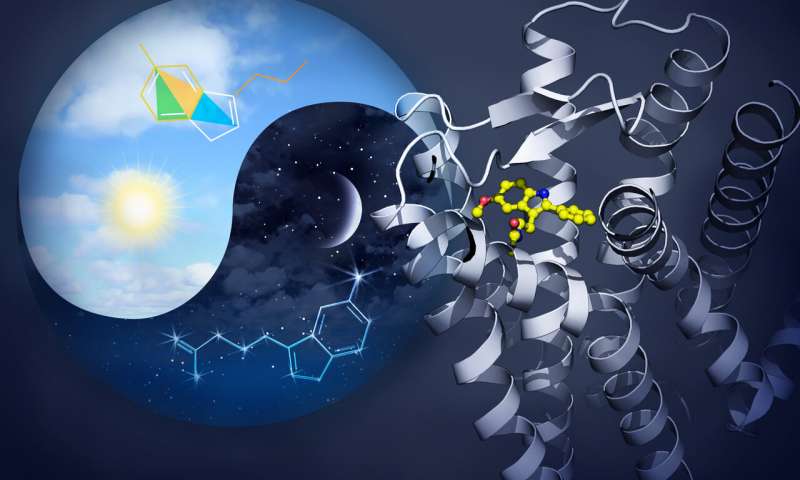
An international team of researchers used an X-ray laser at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory to create the first detailed maps of two melatonin receptors that tell our bodies when to go to sleep or wake...
The strongest synthetic materials are often those that intentionally mimic nature.
One natural substance scientists have looked to in creating synthetic materials is nacre, also known as mother-of-pearl. An exceptionally tough, stiff material produced by some mollusks and serving as their inner shell...
Researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory have created the largest simulation to date of an entire gene of DNA, a feat that required one billion atoms to model and will help researchers to better understand and develop cures for...
A team of scientists including researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has studied a catalyst that decomposes nerve agents, eliminating their harmful and lethal effects. The research was published Friday, April 19, in the Journal...
Surplus industrial carbon dioxide creates an opportunity to convert waste into a valuable commodity. Excess CO2 can be a feedstock for chemicals typically derived from fossil fuels, but the process is energy-intensive and expensive. University of Illinois chemical engineers...