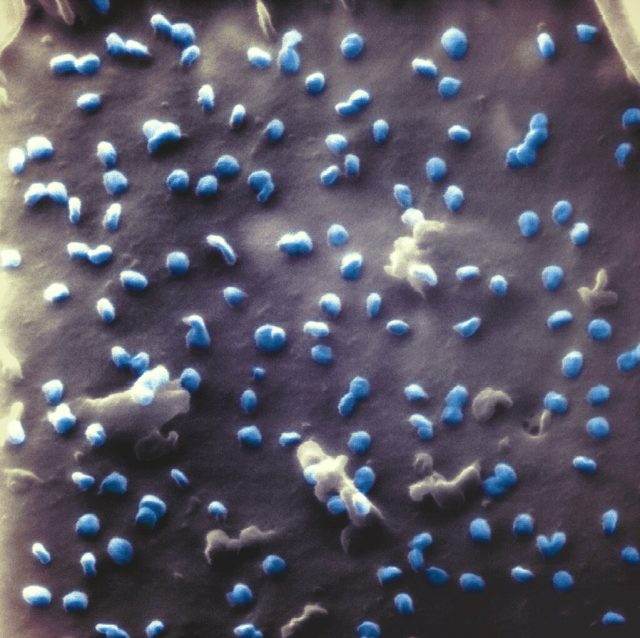
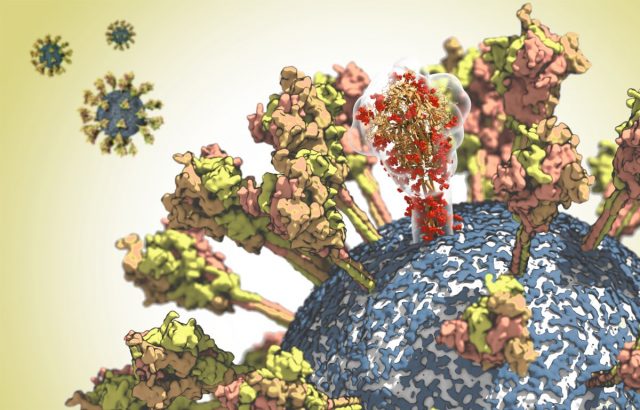
Scientists at Bielefeld University's Faculty of Physics have succeeded for the first time in imaging the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus with a helium ion microscope. In contrast to the more conventional electron microscopy, the samples do not need a thin metal...
Since the beginning of the pandemic, scientists worldwide have been working intensely to precisely characterize the novel SARS-CoV2 virus. Only by understanding in detail how the virus is constructed and how it replicates can targets for effective antiviral medications...
For the first time, scientists have calculated the global impact of human activity on animal movement, revealing widespread impacts that threaten species survival and biodiversity.
While it has been shown that activities such as logging and urbanisation can have big...
As scientists learn more about the microorganisms that colonize the body—collectively called the microbiota—one area of intense interest is the effect that these microbes can have on the brain. A new study led by Salk Institute scientists has identified...
Scientists at EPFL have made breakthrough discoveries on the circadian clock and how it affects gene expression. Some of the findings suggest a biological underpinning for different behaviors in people, such as morning people, nappers, evening people, night owls...
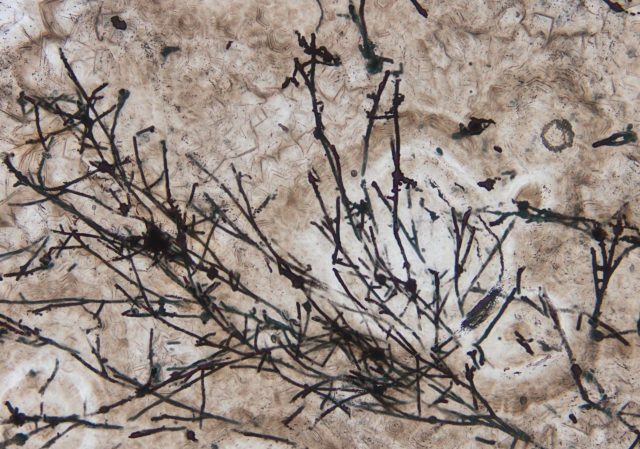
When you think of fungi, what comes to mind may be a crucial ingredient in a recipe or their amazing ability to break down dead organic matter into vital nutrients. But new research by Shuhai Xiao, a professor of...
Organelles continue to thrive after the cells within which they exist die, a team of University of Bristol scientists have found, overturning previous assumptions that organelles decay too quickly to be fossilised.
As described in the journal Sciences Advances today , researchers...
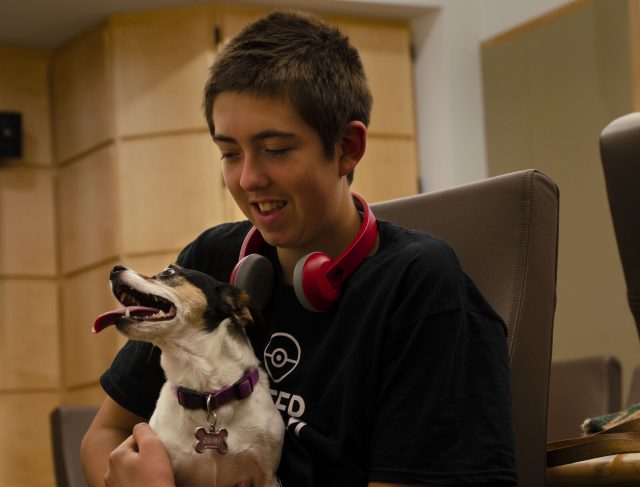
Dogs synchronize their behavior with the children in their family, but not as much as they do with adults, a new study from Oregon State University researchers found.
The findings are important because there is a growing body of evidence...
The popularity of genetic and ancestry services like Ancestry.com and 23andMe attests that people care about where their ancestors originated. The underlying assumption is that the geography of one's forebears affects one's genes today.
Historically, scientists have found that geography...
In a study of 500 sourdough starters spanning four continents, scientists have garnered new insights into the environmental factors that contribute to each sourdough starter's microbial ecosystem, and how different types of microbes influence both a sourdough's aroma and...
Man's best friend might actually belong to a woman.
In a cross-cultural analysis, Washington State University researchers found several factors may have played a role in building the mutually beneficial relationship between humans and dogs, including temperature, hunting and surprisingly...