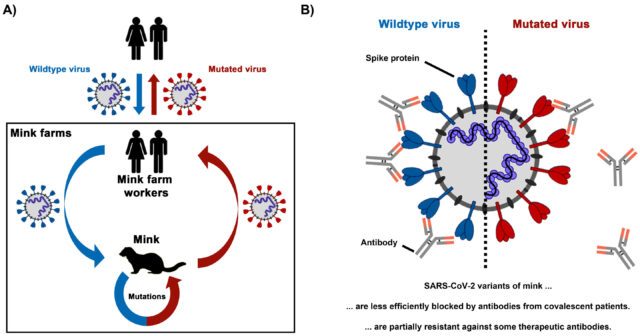
It has been known for about a year that minks can become infected with SARS-CoV-2. The virus had been transmitted from humans to farmed mink and mutated in infected animals. Mutations were acquired in the spike protein, which is...
Canadian researchers have discovered a new and direct molecular mechanism to stop cancer cells from proliferating. In the prestigious journal Nature Cell Biology, scientists from Université de Montréal show that a disruption of a fine balance in the composition...
On a certain level, extinction is all about energy. Animals move over their surroundings like pacmen, chomping up resources to fuel their survival. If they gain a certain energy threshold, they reproduce, essentially earning an extra life. If they...
In a report published today in Nature Communications, a surprising new genetic discovery by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh suggests that there may be molecular switches that control lifespan and...
Green algae that evolved to tolerate hostile and fluctuating conditions in salt marshes and inland salt flats are expected to survive climate change, thanks to hardy genes they stole from bacteria, according to a Rutgers-led study.
These Picochlorum single-celled species...
When anthropologists consider the origins of warfare, their evolutionary theories tend to boil it down to the resource-scarcity trifecta of food, territory and mates—three resources that would justify the loss of life and risk to a warring group of...
Once, single-cell life claimed sole dominion over the earth. For some three billion years, unfathomable generations of unicellular organisms ate, grew and reproduced among only each other. They evolved into predators and prey, thrived and spread across the primordial...
People with blood type O often get more severely ill from cholera than people of other blood types. New research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis may explain why.
In people with blood type O, scientists found...
Grocery store aisles are stocked with products that promise to kill bacteria. People snap up those items to protect themselves from the germs that make them sick. However, new research from Washington University in St. Louis finds that a...
It's like something out of science fiction. Research led by Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences has revealed that a group of microbes, which feed off chemical reactions triggered by radioactivity, have been at an evolutionary standstill for millions of...
A serial electron microscopy reconstruction of a single synaptic connection.
Credit: Image courtesy of The Scripps Research Institute
Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in La Jolla have revealed new clues to the wiring of the brain. A team led...