Fractured rocks of impact craters have been suggested as suitable environments for deep colonization of microbial communities. In a new study published in Communications Earth & Environment, a team of researchers shows that fungi has colonized deep parts of the...
A mutation in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2—one of several genetic mutations in the concerning variants that have emerged in the United Kingdom, South Africa, and Brazil—makes the virus up to eight times more infectious in human cells than...
The use of weed killers can increase the prevalence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in soil, a new study from the University of York shows.
Herbicides are one of the most widely used chemicals in agriculture and while these compounds are...
Videos allowing us to see for the first time how small circles of DNA adopt dance-like movements inside a cell have been developed by researchers at universities in Yorkshire.
The footage, developed by a team of scientists from the Universities...
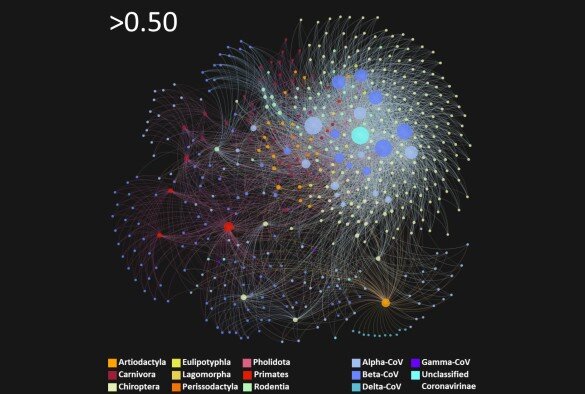
The potential scale of novel coronavirus generation in wild and domesticated animals may have been highly underappreciated, suggests new University of Liverpool research.
Published in Nature Communications, the machine-learning study identifies mammals that are potential sources for generating new coronaviruses, including...
An international team of scientists has determined how harmless E. coli gut bacteria in chickens can easily pick up the genes required to evolve to cause a life-threatening infection. Their study, published in Nature Communications, warns that such infections not...
Genes that determine the shape of a person's facial profile have been discovered by a UCL-led research team.
The researchers identified 32 gene regions that influenced facial features such as nose, lip, jaw, and brow shape, nine of which were entirely new...
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have gained new insight into the biological processes of a chytrid fungus responsible for a deadly skin infection devastating frog populations worldwide.
Led by cell biologist Lillian Fritz-Laylin, the team describes in a...
Under increasing global warming, tropical fish are escaping warmer seas by extending their habitat ranges towards more temperate waters.
But a new study from the University of Adelaide, published in Nature Climate Change, shows that the ocean acidification predicted under continuing high CO2 emissions...
New research out of the University of Chicago has found evidence that the lobe-finned fish species Tiktaalik roseae was capable of both biting and suction during feeding, similar to modern-day gars. These results, published on Feb. 1 in the Proceedings...
Hydrocarbons and petroleum are almost synonymous in environmental science. After all, oil reserves account for nearly all the hydrocarbons we encounter. But the few hydrocarbons that trace their origin to biological sources may play a larger ecological role than...