People aren't the only ones who show sympathy. Birds also seem to care about the fate of conspecifics. They notice how much food the others already have and then share theirs with individuals that were not given any. "They...
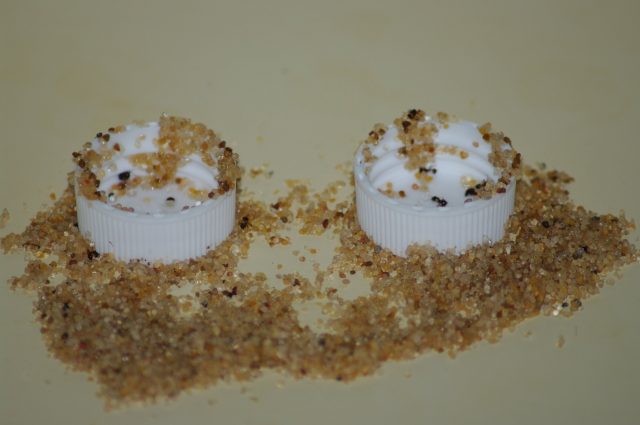
Researchers have observed black imported fire ants using sand to draw liquid food out of containers, when faced with the risk of drowning. This is the first time this sophisticated tool use has been reported in animals. These findings...
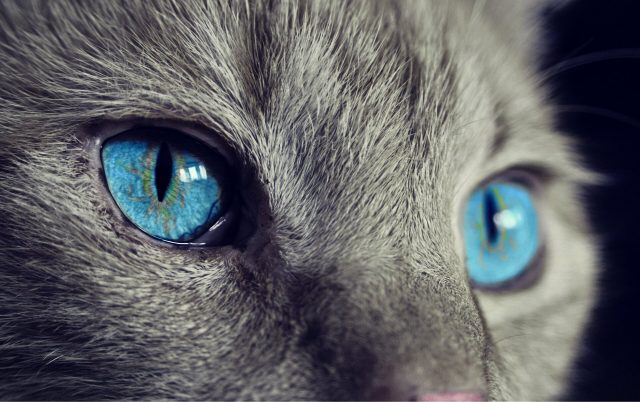
A team of psychologists at the Universities of Sussex and Portsmouth have purr-fected the art of building a bond with cats.
The new study "The role of cat eye narrowing movements in cat-human communication," published online in the Nature journal Scientific...
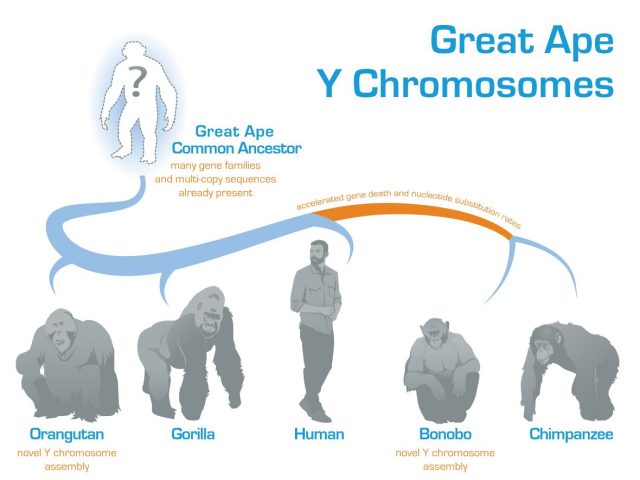
New analysis of the DNA sequence of the male-specific Y chromosomes from all living species of the great ape family helps to clarify our understanding of how this enigmatic chromosome evolved. A clearer picture of the evolution of the...
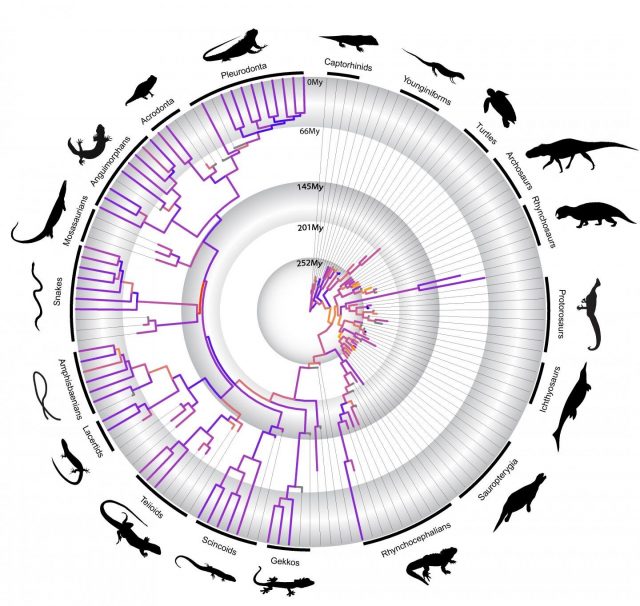
Challenging a 75-year-old notion about how and when reptiles evolved during the past 300 million-plus years involves a lot of camerawork, loads of CT scanning, and, most of all, thousands of miles of travel. Just check the stamps in...
Though some believe prehistoric humans lived in harmony with nature, a new analysis of fossils shows human arrival in the Bahamas caused some birds to be lost from the islands and other species to be completely wiped out.
The researchers...
A new study shows that the body size of the iconic gigantic or megatooth shark, about 15 meters (50 feet) in length, is indeed anomalously large compared to body sizes of its relatives.
Formally called Otodus megalodon, the fossil shark...
The carnivorous plant Venus flytrap (Dionaea muscipula) captures and digests small animals and absorbs nutrients with its characteristic insectivorous leaves. Six sensory hairs on the inner surface of each leaf sense a visiting prey and cause the trap to...
By placing 3-D-printed and GPS-enabled decoy sea turtle eggs into nests on the beach, it's possible to gather key evidence needed to expose rampant illegal trade of the eggs, suggests a study publishing in the journal Current Biology on October 5....
As kids, we learn there are four seasons, but researchers at the Stanford School of Medicine have found evidence to suggest that the human body doesn't see it this way.
"We're taught that the four seasons—winter, spring, summer and fall—are...
A group led by researchers at Butantan Institute in Brazil and supported by FAPESP has described for the first time the presence of venom glands in the mouth of an amphibian. The legless animal is a caecilian and lives...