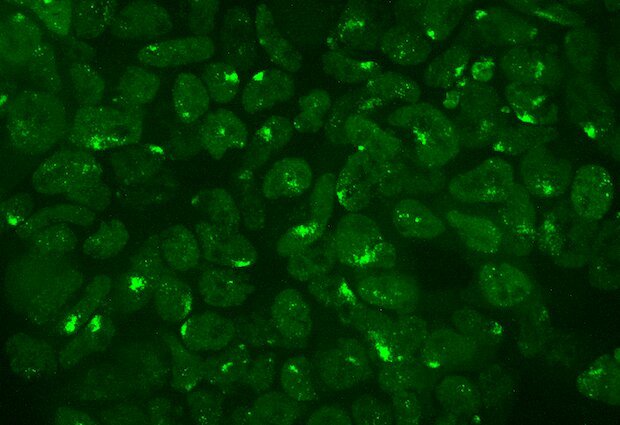
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and Institut Curie in Paris have shown that the protein SPEN plays a crucial role in the process of X-chromosome inactivation, whereby female mammalian embryos silence gene expression on...
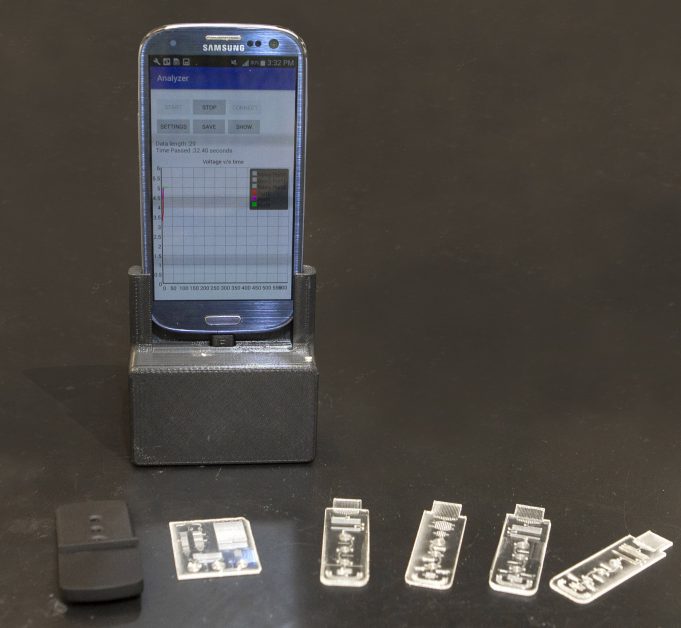
Engineers with the University of Cincinnati have created a tiny portable lab that plugs into your phone, connecting it automatically to a doctor's office through a custom app UC developed.
The lab the size of a credit card can diagnose...
Methanol is a versatile and efficient chemical used as fuel in the production of countless products. Carbon dioxide (CO2), on the other hand, is a greenhouse gas that is the unwanted byproduct of many industrial processes.
Converting CO2 to methanol...
While eating takeout one day, University of Chicago scientists Bozhi Tian and Yin Fang started thinking about the noodles—specifically, their elasticity. A specialty of Xi'an, Tian's hometown in China, is wheat noodles stretched by hand until they become chewy—strong...
New research by engineers at MIT and elsewhere could lead to batteries that can pack more power per pound and last longer, based on the long-sought goal of using pure lithium metal as one of the battery's two electrodes,...
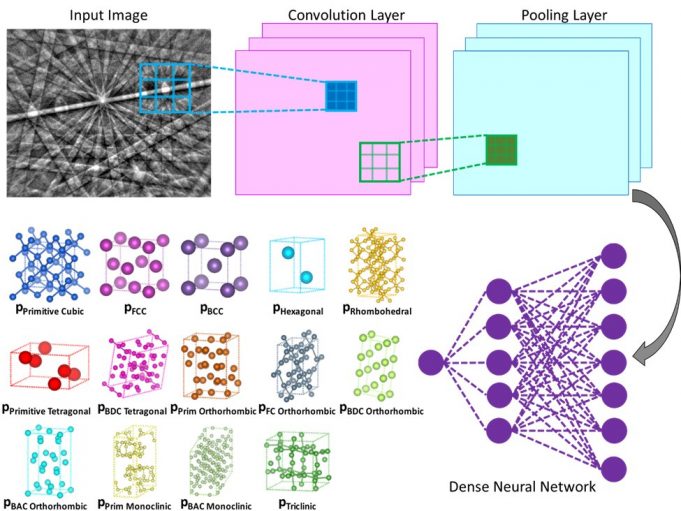
Nanoengineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a computer-based method that could make it less labor-intensive to determine the crystal structures of various materials and molecules, including alloys, proteins and pharmaceuticals. The method uses a machine...
Patients with diabetes have to test their blood sugar levels several times a day to make sure they are not getting too high or too low. Studies have shown that more than half of patients don't test often enough,...
The materials the United States and other countries plan to use to store high-level nuclear waste will likely degrade faster than anyone previously knew because of the way those materials interact, new research shows.
The findings, published today in the...
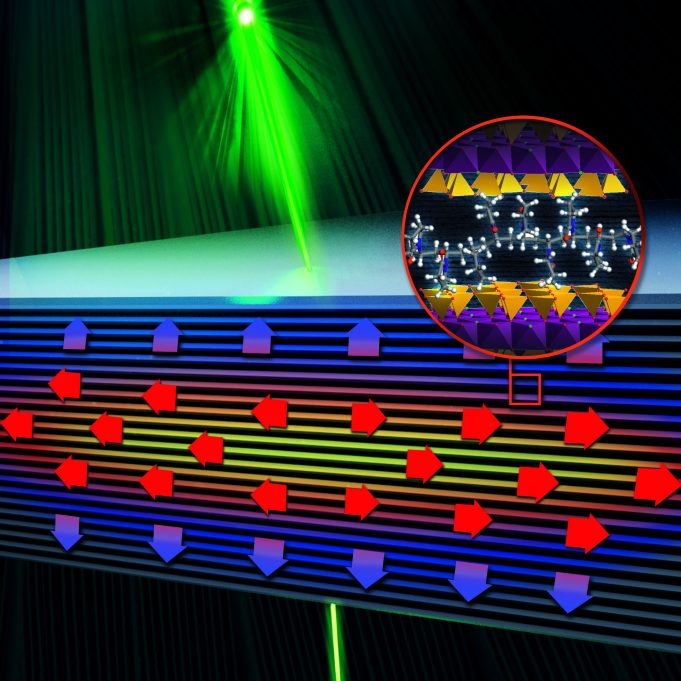
We've all heard, and seen, how a picture paints a thousand words. Now, in a scientific twist on that saying, researchers at the Florida State University-headquartered National High Magnetic Field Laboratory (National MagLab), are creating pictures that paint thousands...
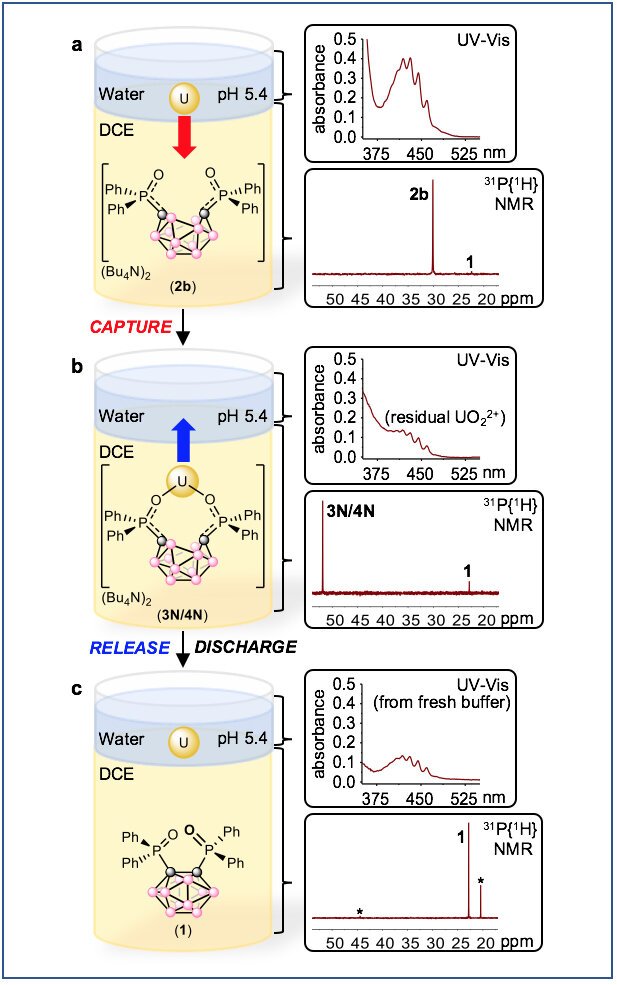
Fifty years ago, scientists hit upon what they thought could be the next rocket fuel. Carboranes—molecules composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms clustered together in three-dimensional shapes—were seen as the possible basis for next-generation propellants due to their...
Styrofoam or copper—both materials have very different properties with regard to their ability to conduct heat. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPI-P) in Mainz and the University of Bayreuth have now jointly developed and characterized...