Researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science at the University of Tokyo sifted through experimental data to probe the possibility that supercooled water has a liquid-to-liquid phase transition between disordered and tetrahedrally structured forms. They found evidence of a...
By applying natural language processing tools to the movements of protein molecules, University of Maryland scientists created an abstract language that describes the multiple shapes a protein molecule can take and how and when it transitions from one shape...
To solve a 100-year puzzle in metallurgy about why single crystals show staged hardening while others don't, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists took it down to the atomistic level.
The research appears in the Oct. 5 edition of Nature Materials.
For...
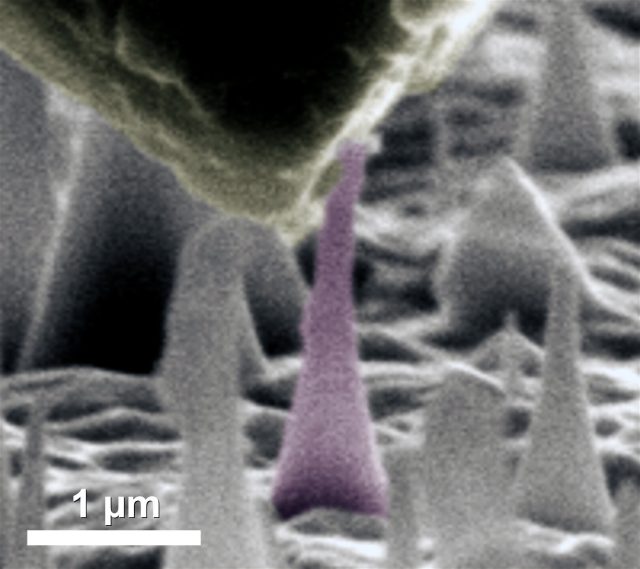
Long known as the hardest of all natural materials, diamonds are also exceptional thermal conductors and electrical insulators. Now, researchers have discovered a way to tweak tiny needles of diamond in a controlled way to transform their electronic properties,...
A group of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory has discovered a way to convert a common byproduct of the paper manufacturing process into valuable chemical precursors for making nylon. The process is much more environmentally...
Researchers at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering have made new discoveries on the effects of temperature on sustainable polymers. Their findings may help the industry to produce plastics that are better for the environment.
"Plastics made from petroleum, a non-renewable...
A new 3-D-printing method will make it easier to manufacture and control the shape of soft robots, artificial muscles and wearable devices. Researchers at UC San Diego show that by controlling the printing temperature of liquid crystal elastomer, or...
Metals such as iron and calcium play a crucial role inside the human body, so it's no surprise that bioengineers would like to integrate them into the soft, stretchy materials used to repair skin, blood vessels, lungs and other...
In the search for clean energy alternatives to fossil fuels, one promising solution relies on photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells—water-splitting, artificial-photosynthesis devices that turn sunlight and water into solar fuels such as hydrogen.
In just a decade, researchers in the field have...
Researchers from UCLA and China have found that catalase, a naturally occurring enzyme, holds potential as a low-cost therapeutic drug to treat COVID-19 symptoms and suppress the replication of coronavirus inside the body. A study detailing the research was...
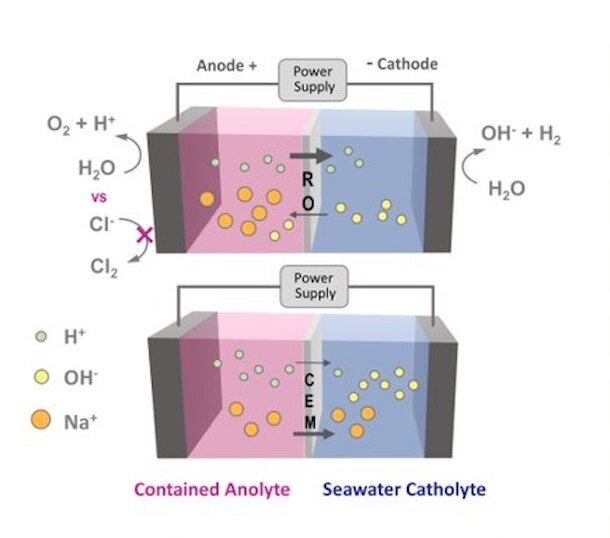
The power of the sun, wind and sea may soon combine to produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel, according to a team of Penn State researchers. The team integrated water purification technology into a new proof-of-concept design for a sea water...