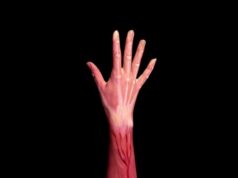
In this electron microscope image of fish muscle, the muscle fiber is removed showing the mesh of surrounding connective tissue. Credit: David Sleboda/Brown University
Touch your toes. Feel that familiar tension in your leg muscles? A new Brown University study suggests that one source of the tension might be something that scientists have always known was in your muscle fibers, but never accounted for: fluid.
In every animal, including humans, each muscle fiber is both filled with incompressible fluid and sheathed in a winding mesh of collagen connective tissue. When a muscle stretches in length, the surrounding mesh lengthens and becomes narrower in diameter.
What follows is like what happens in one of those woven “finger trap” toys, reports doctoral student David Sleboda, lead author of the study published in Biology Letters. Just like the toy squeezes your sheathed fingers when you stretch it far enough, the collagen mesh eventually squeezes down on the muscle fiber. Because the fiber is full of incompressible fluid, Sleboda discovered, it’s volume pushes back against the narrowing mesh, creating a tension that makes further stretch much more difficult.
“The fundamental problem here is a conflict of volumes,” Sleboda said. “The mesh sleeve can change volume but the fiber is a constant volume. Eventually the two are going to run into each other and that’s where you see the tension really shoot up.”
Find your dream job in the space industry. Check our Space Job Board »
Other previously posited factors also contribute to the tension you feel when you stretch, Sleboda acknowledged. One is tension created by kinks in the collagen mesh itself and another is a stretchy protein in muscle fibers called titin. But the fluid-filled nature of muscle fibers appear to play a role, too.
A model and a muscle
Sleboda works in the lab of study co-author Thomas Roberts, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology who studies muscle structure and performance. Sleboda was looking at electron microscope pictures of animal muscle fibers and their collagen sheaths, and decided to build a simple model himself (he also made his own microscope pictures, including one that recently earned a featured mention on the blog of NIH director Francis Collins).
Materials for Sleboda’s model weren’t hard to come by. The collagen mesh is well simulated by Techflex braided sheathing (typically used to neatly bundle computer cables together) and the muscle fiber could be made from a water-filled condom bought at the corner drug store.
Rather quickly the model revealed that the fluid played a significant role in the mechanical properties of the muscle – the resistance of the water-filled condom made the Techflex harder to stretch. Scientists have rarely modeled muscle mechanics to account for fluid in the fibers, Sleboda said. They had largely assumed that the fluid played only a chemical role within cells.
But did Sleboda’s model really say anything meaningful about actual physiology? He conducted experiments to find out. In the study, Sleboda and Roberts report careful measurements of lengthwise stretch and the resulting tension in not only the model, but also in real bullfrog muscle as they varied the amounts of fluid in the muscle fibers (and the condoms).
The model and the real muscle both displayed the same characteristic curve in their plots: The more fluid volume in the muscle fibers, the more tension for a given length of stretch. The fluid makes a specific, measurable, mechanical difference.
“We could get the exact same behavior using just a simple model,” Sleboda said. “Our study provides the first empirical evidence of fluid influencing muscle tension.”
Sleboda said his findings argue for accounting for fluid in models of muscle mechanics. For example, after exercise muscle fibers appear to take on more fluid. Adding fluid’s effects to models of muscle behavior could then improve understanding of how muscles behave after exercise.
There are also medical conditions that affect how the collagen mesh is structured or performs, Sleboda said. Knowing how it interacts with fluid-filled muscle fibers could also prove important in future research.
Studies in other areas of animal physiology provide a ready-made roadmap, in fact, because fiber-reinforced fluid cavities, called “hydrostatic skeletons” arecommon structural elements in some organisms, Sleboda said. It’s not a stretch to think the lessons learned there, could now be applied to studying muscle.
Source: Brown University
Journal Reference:
Incompressible fluid plays a mechanical role in the development of passive muscle tension, Biology Letters, rsbl.royalsocietypublishing.org/lookup/doi/10.1098/rsbl.2016.0630