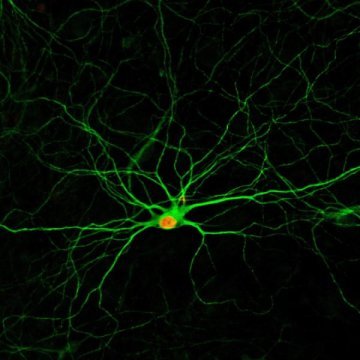
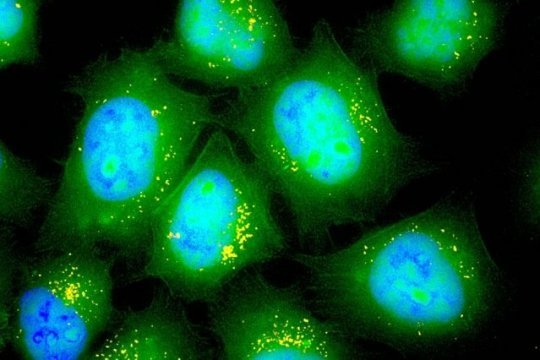
A simple drug cocktail that converts cells neighboring damaged neurons into functional new neurons could potentially be used to treat stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and brain injuries. A team of researchers at Penn State identified a set of four, or...
The old adage "use it or lose it" tells us: if you stop using your muscles, they'll shrink. Until recently, scientists thought this meant that nuclei—the cell control centers that build and maintain muscle fibers—are also lost to sloth.
But...
Prof. Rony Paz of the Weizmann Institute of Science suggests that our brains are like modern washing machines—evolved to have the latest sophisticated programming, but more vulnerable to breakdown and prone to develop costly disorders. He and a group...
The size of children's heads is not only related to the growth of their skull, but also their brain. A genome-wide analysis, published in Nature Communications, now reports the largest known genetic effects on head circumference and the related...
Scientists say they can predict whether a person can expect to live longer or die sooner than average, by looking at their DNA.
The team has analysed the combined effect of genetic variations that influence lifespan to produce a scoring...
By combining deep learning algorithms and statistical methods, investigators from the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE), the Centro Nacional de Análisis Genómico (CNAG-CRG) of the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) and the Institute of Genomics at the University of...
Messenger RNA, which can induce cells to produce therapeutic proteins, holds great promise for treating a variety of diseases. The biggest obstacle to this approach so far has been finding safe and efficient ways to deliver mRNA molecules to...
Materials are widely used to help heal wounds: Collagen sponges help treat burns and pressure sores, and scaffold-like implants are used to repair bones. However, the process of tissue repair changes over time, so scientists are developing biomaterials that...
There is no compelling evidence to indicate important health benefits of non-sugar sweeteners, and potential harms cannot be ruled out, suggests a review of published studies in The BMJ today.
Growing concerns about health and quality of life have encouraged...
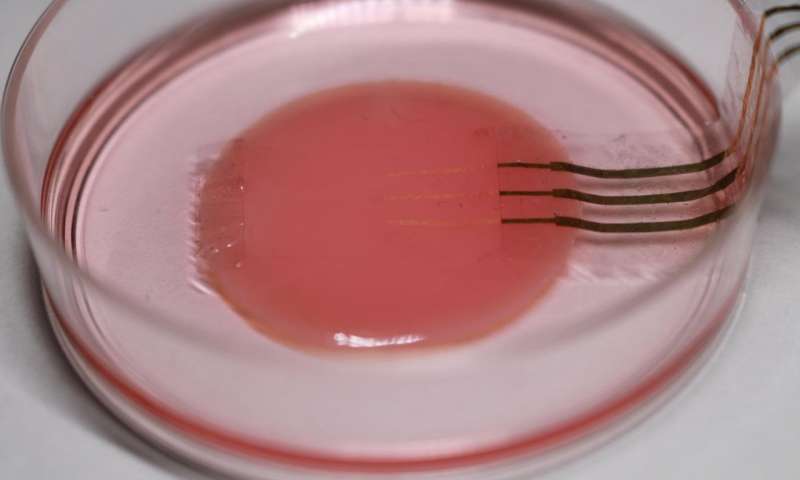
For the first time, engineers have demonstrated an electronic device to monitor beating heart cells without affecting their behavior. A collaboration between the University of Tokyo, Tokyo Women's Medical University and RIKEN in Japan produced a functional sample of...
Researchers analysing soil from Ireland long thought to have medicinal properties have discovered that it contains a previously unknown strain of bacteria which is effective against four of the top six superbugs that are resistant to antibiotics, including MRSA.
Antibiotic...