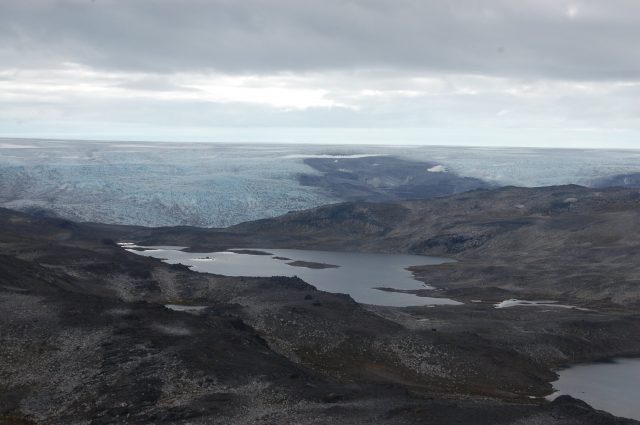
In 1966, US Army scientists drilled down through nearly a mile of ice in northwestern Greenland -- and pulled up a fifteen-foot-long tube of dirt from the bottom. Then this frozen sediment was lost in a freezer for decades....
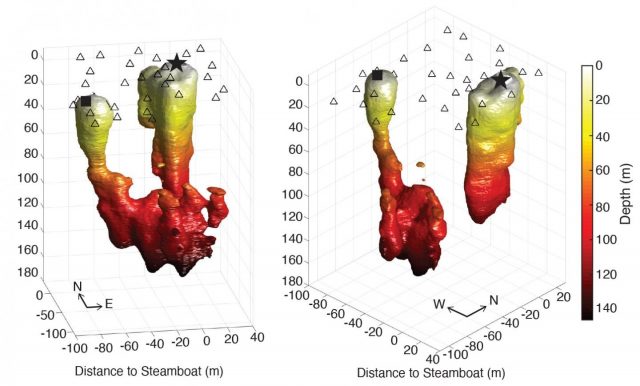
When Steamboat Geyser, the world's tallest, started erupting again in 2018 in Yellowstone National Park after decades of relative silence, it raised a few tantalizing scientific questions. Why is it so tall? Why is it erupting again now? And...
Recent summer droughts in Europe are far more severe than anything in the past 2,100 years, according to a new study.
An international team, led by the University of Cambridge, studied the chemical fingerprints in European oak trees to reconstruct...
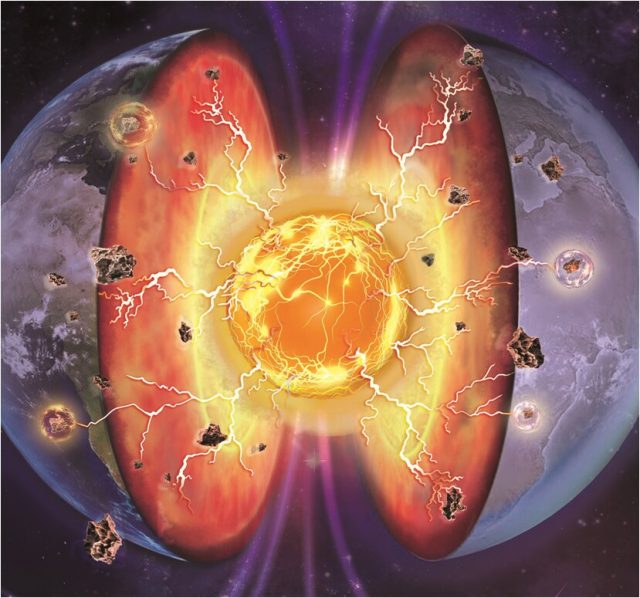
New research led by the University of Cambridge has found rare evidence -- preserved in the chemistry of ancient rocks from Greenland -- which tells of a time when Earth was almost entirely molten.
The study, published in the journal Science...
Pierfranco Demontis said in 1988, "Ice becomes a fast-ion conductor at high pressure and high temperatures," but his prediction was only hypothetical until recently. After 30 years of study, superionic water ice was verified experimentally in 2018. Superionicity may...
Large tropical volcanos have caused some of the world's most destructive natural disasters in history, with eruptions spewing out massive quantities of harmful gases and other debris that can wipe out everything in their path.
But what about wider impacts...
It's no secret that the United States' $13 billion cannabis industry is big business. Less obvious to many is the environmental toll this booming business is taking, in the form of greenhouse gas emissions from commercial, mostly indoor production.
A...
The economic benefits of conserving or restoring natural sites "outweigh" the profit potential of converting them for intensive human use, according to the largest-ever study comparing the value of protecting nature at particular locations with that of exploiting it.
A...
A study by Monash scientists has found that a rare earth affects the fate of a key reaction with copper, gold, silver, and uranium mineralisation.
The work is part of the "Olympic Dam in a test tube" project, where researchers...
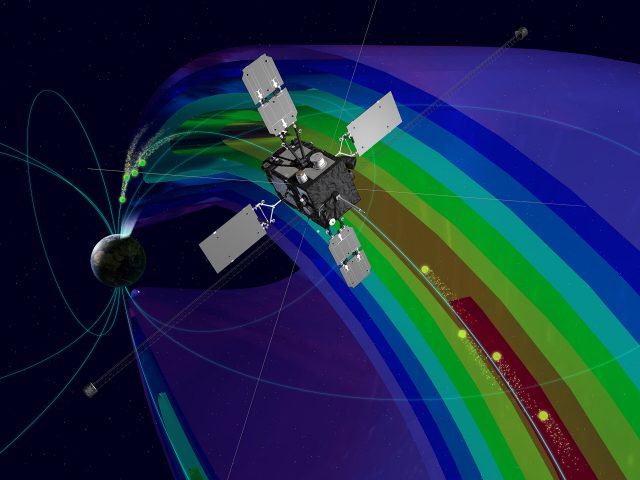
A critical ingredient for auroras exists much higher in space than previously thought, according to new research in the journal Scientific Reports. The dazzling light displays in the polar night skies require an electric accelerator to propel charged particles down...
Nuisance flooding has increased on U.S. coasts in recent decades due to sea level rise, and new research co-authored by the University of Central Florida uncovered an additional reason for its added frequency.
In a study appearing today in the...