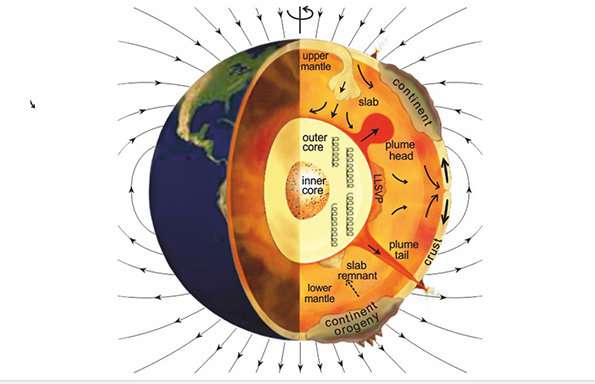
Scientists have discovered fresh insights into the metallic core at the centre of our planet.
The findings could aid understanding of how the Earth was formed from elements in space, some 10 billion years ago.
They could also shed light on...
The evolution of Earth's first animals more than 500 million years ago caused global warming, new research shows.
Some 520-540 million years ago, animal life evolved in the ocean and began breaking down organic material on the seafloor, leading to...
A new study has revealed sensitive regions of the world are still at risk from the dangerous and potentially irreversible effects of climate change; even if we meet the target of not increasing global temperature above 1.5°C over the...
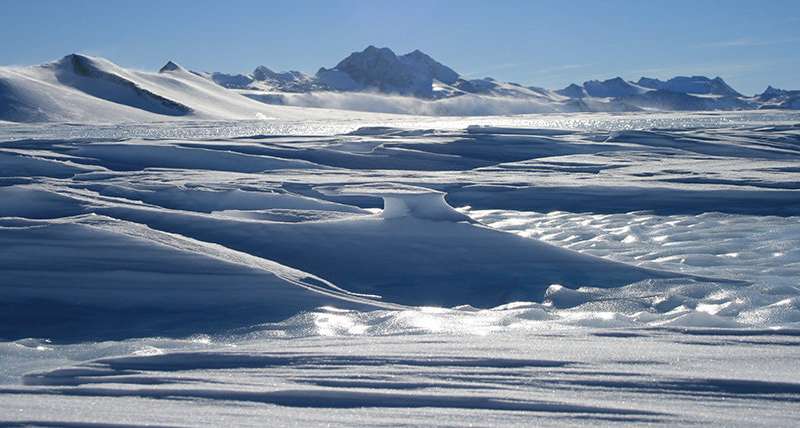
A researcher from the University of Rhode Island's Graduate School of Oceanography and five other scientists have discovered an active volcanic heat source beneath the Pine Island Glacier in Antarctica.
The discovery and other findings, which are critical to understanding...
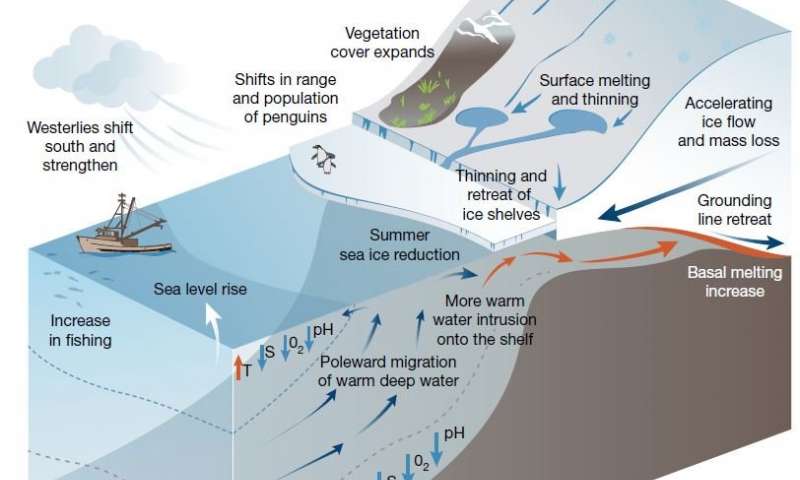
Decisions made in the next decade will determine whether Antarctica suffers dramatic changes that contribute to a metre of global sea level rise.
In a new study, scientists argue that time is running out to save this unique ecosystem, and...
Global climate change, fueled by skyrocketing levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide, is siphoning oxygen from today's oceans at an alarming pace—so fast that scientists aren't entirely sure how the planet will respond.
Their only hint? Look to the past.
In a...
Understanding how climate has changed over the last centuries and will evolve in the future requires a detailed knowledge of all the climate system components, including an accurate evaluation of the effect of human activity on those.
Assessing the effect...
A new study by the University of Liverpool, in collaboration with the Universities of Lancaster and Oslo, sheds light on a longstanding question that has puzzled earth scientists.
Using previously unavailable data, scientists at the University confirm a correlation between...
An invisible layer of biological compounds on the sea surface reduces the rate at which carbon dioxide gas moves between the atmosphere and the oceans, scientists have reported.
Surfactants are organic compounds produced by marine plankton and bacteria that form...
The sky sometimes has its limits, according to new research from two University of Chicago atmospheric scientists.
A study published May 24 in Science offers an explanation for a mysterious and sometimes deadly weather pattern in which the jet stream,...
For decades, scientists have conducted research centered around the five major mass extinctions that have shaped the world we live in. The extinctions date back more than 450 million years with the Late Ordovician Mass Extinction to the deadliest...