Injecting particles into the atmosphere to cool the planet and counter the warming effects of climate change would do nothing to offset the crop damage from rising global temperatures, according to a new analysis by University of California, Berkeley,...
Early Earth was a hot, gaseous, dusty and dynamic planet with an atmosphere and an ocean. Then its surface cooled and stabilized enough for clouds, landmasses and early life to form about four billion years ago, during what's called...
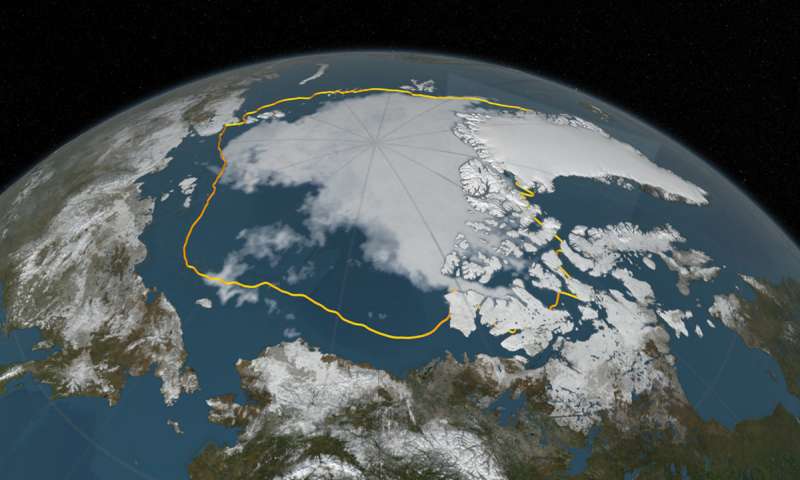
New research, led by former Carnegie postdoctoral fellow Summer Praetorius, shows that changes in the heat flow of the northern Pacific Ocean may have a larger effect on the Arctic climate than previously thought. The findings are published in...
Hurricane Harvey was an unprecedented rain event that delivered five consistent days of flooding and storms to Texas last August. Now, research from UTSA Assistant Professor Vikram Kapoor in civil and environmental engineering has substantiated that the storm caused...
Supervolcanoes are one of Mother Nature's deadliest phenomena, and when they erupt, they can change the climate of the entire planet.
To get a glimpse for how future catastrophic volcanic events might alter our lives, scientists at the University of...
The oceans are the planet's most important depository for atmospheric carbon dioxide on time scales of decades to millenia. But the process of locking away greenhouse gas is weakened by activity of the Southern Ocean, so an increase in...
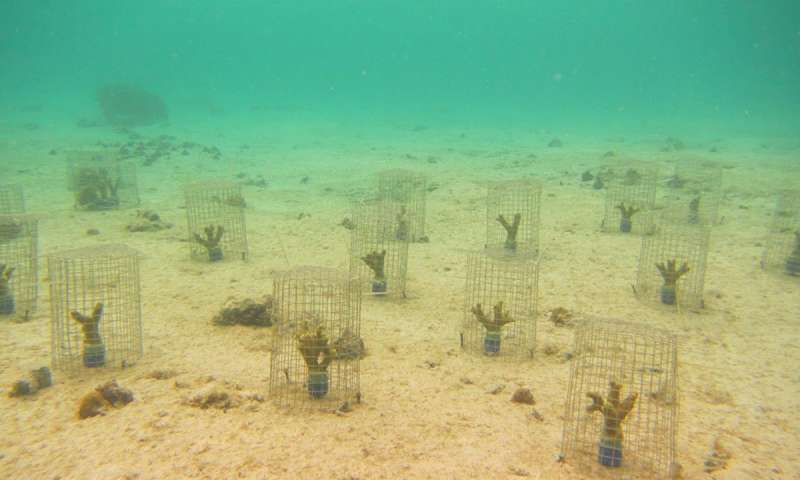
A previously overlooked predator— a thumbnail-sized snail—could be increasing the pressure on coral reefs already weakened by the effects of overfishing, rising ocean temperatures, pollution and other threats. The snail attacks a key coral species that may offer the...
The long-dormant Yellowstone super-volcano in the American West has a different history than previously thought, according to a new study by a Virginia Tech geoscientist.
Scientists have long thought that Yellowstone Caldera, part of the Rocky Mountains and located mostly...
For decades, researchers believed the Western Hemisphere was settled by humans roughly 13,500 years ago, a theory based largely upon the widespread distribution of Clovis artifacts dated to that time. Clovis artifacts are distinctive prehistoric stone tools so named...
With four years of data from 268 seismometers on the ocean floor and several hundred on land, researchers have found anomalies in the upper mantle below both ends of the Cascadia Subduction Zone. They may influence the location, frequency...
The bad news: Dust from the Sahara Desert in Africa—totaling a staggering 2 to 9 trillion pounds worldwide—has been almost a biblical plague on Texas and much of the Southern United States in recent weeks. The good news: the...