Wells that extract natural gas from underground often leak large amounts of methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, into the air. A team of Princeton University researchers has found that, in one of the biggest gas-producing regions, most of these...
The remains of a microscopic drop of ancient seawater has assisted in rewriting the history of Earth's evolution when it was used to re-establish the time that plate tectonics started on the planet.
Plate tectonics is Earth's vital—and unique—continuous recycling...
Within a shrouded New Zealand forest, a tree stump keeps itself alive by holding onto the roots of its neighboring trees, exchanging water and resources through the grafted root system. New research, publishing July 25 in iScience, details how surrounding...
The discovery of Tamu Massif, a gigantic volcano located about 1,000 miles east of Japan, made big news in 2013 when researchers reported it was the largest single volcano documented on earth, roughly the size of New Mexico.
New findings,...
Volatile elements in magma, primarily water, drive explosive volcanic eruptions. The tricky part is determining just how much volatile content was present before the eruption took place. This is especially difficult when the only evidence scientists have to go...
For years, scientists have pointed to warming permafrost in the Arctic tundra as a source for increased carbon in the atmosphere; as this soil warms, it releases greenhouse gases that have long been trapped in frozen ground.
New research from...
As a nation "girt by sea," Australians live with the joy and risks of the ocean.
We swim, we surf, we sail and we fish. And rock fishing is something around 1.2 million Australians enjoy doing.
But over the past 13 years, Surf...
For the first time, researchers at the University of Michigan have detected bromine atoms in the atmosphere, and in doing so, have confirmed the reaction pathway through which mercury is removed from the atmosphere and enters the ecosystem in...
A new radioactivity model of Earth's ancient rocks calls into question current models for the formation of Earth's continental crust, suggesting continents may have risen out of the sea much earlier than previously thought but were destroyed, leaving little...
Thousand-year-old tropical soil unearthed by accelerating deforestation and agriculture land use could be unleashing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, according to a new study from researchers at Florida State University.
In an investigation of 19 sites in the eastern Democratic...
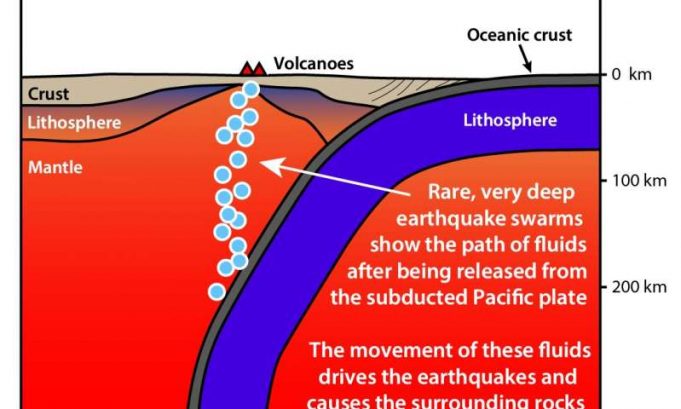
Deep under the ocean bed, a sinking tectonic plate causes a "swarm" of earthquakes, feeding molten rock into newly forming volcanoes, new research has discovered.
Earthquake swarms are when a large number of earthquakes occur close together over a short...