The sinking carcasses of fish from near-surface waters deliver toxic mercury pollution to the most remote and inaccessible parts of the world's oceans, including the deepest spot of them all: the 36,000-foot-deep Mariana Trench in the northwest Pacific.
And most...
Curtin University research has shed new light on when one of the largest mass extinction events on Earth occurred, which gives new meaning to what killed Triassic life and allowed the ecological expansion of dinosaurs in the Jurassic period.https://secureframe.doubleclick.net/container.html?ecs=20201117
The...
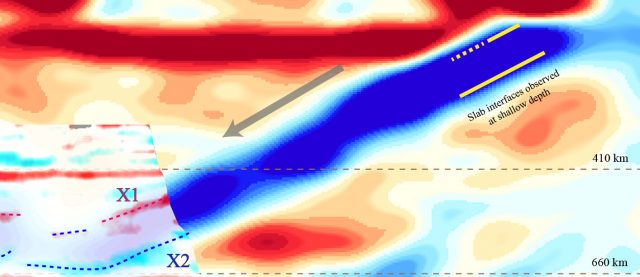
In a study that gives new meaning to the term "rock bottom," seismic researchers have discovered the underside of a rocky slab of Earth's surface layer, or lithosphere, that has been pulled more than 400 miles beneath northeastern China...
Vibrations travel through our planet in waves, like chords ringing out from a strummed guitar. Earthquakes, volcanoes and the bustle of human activity excite some of these seismic waves. Many more reverberate from wind-driven ocean storms.
As storms churn the...
A team of European researchers discovered a new high-pressure mineral in a lunar meteorite which is helping to explain what happens to materials within the extreme pressures of the Earth's mantle.
The new mineral donwilhelmsite is the first high-pressure mineral...
A study published today in the journal Science Advances has revealed that the United States ranks as high as third among countries contributing to coastal plastic pollution when taking into account its scrap plastic exports as well as the latest figures...
A new normal is taking shape as a warming planet is changing hurricane behaviors and patterns. Research over the last decade has shown alarming trends resulting in more destructive hurricanes. Global trends suggest hurricanes are getting stronger, moving more...
An international team of coastal scientists has dismissed suggestions that half the world's beaches could become extinct over the course of the 21st century.
The claim was made by European researchers in a paper published in Nature Climate Change in March 2020...
Current understanding is that the chemical composition of the Earth's mantle is relatively homogeneous. But experiments conducted by ETH researchers now show that this view is too simplistic. Their results solve a key problem facing the geosciences—and raise some...
The existence of a tectonic plate called Resurrection has long been a topic of debate among geologists, with some arguing it was never real. Others say it subducted—moved sideways and downward—into the earth's mantle somewhere in the Pacific Margin...
Life on Earth has a long, but also an extremely turbulent history. On more than one occasion, the majority of all species became extinct and an already highly developed biodiversity shrank to a minimum again, changing the course of...