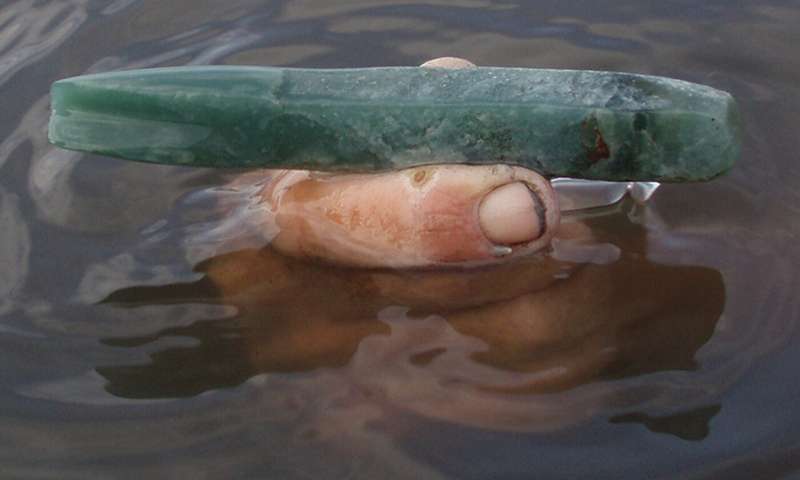
Anthropologists discovered a tool made out of high-quality translucent jadeite with an intact rosewood handle at a site where the ancient Maya processed salt in Belize. The discovery of these high-quality materials—jadeite and rosewood—used as utilitarian tools, demonstrates that...
A 24-tonne dinosaur may have walked in a 'high-heeled' fashion, according to University of Queensland research.
UQ Ph.D. candidate Andréas Jannel and colleagues from UQ's Dinosaur Lab analysed fossils of Australia's only named Jurassic sauropod, Rhoetosaurus brownei, to better understand how...
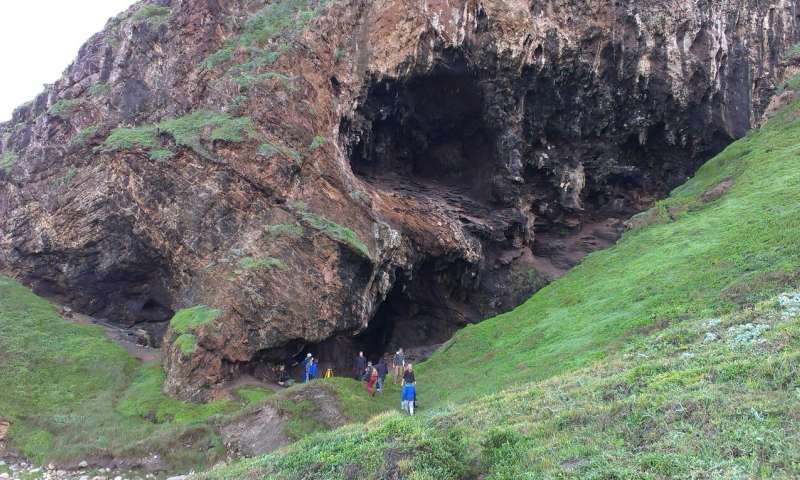
New discoveries made at the Klasies River Cave in South Africa's southern Cape, where charred food remains from hearths were found, provide the first archaeological evidence that anatomically modern humans were roasting and eating plant starches, such as those...
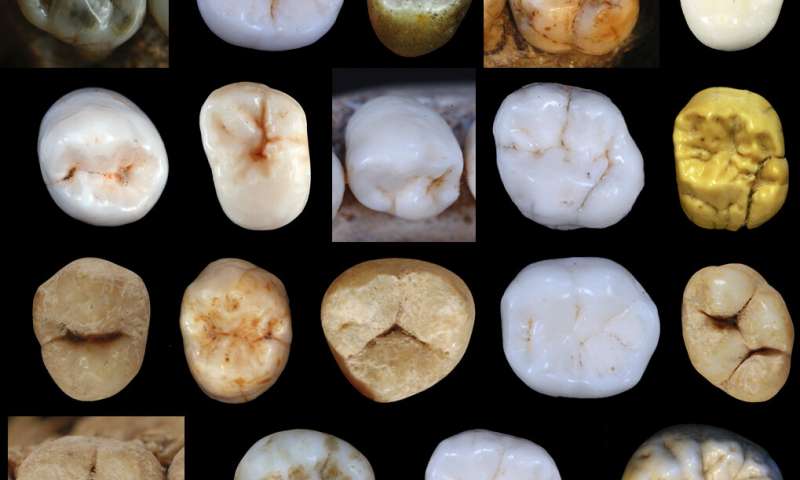
Neanderthals and modern humans diverged at least 800,000 years ago, substantially earlier than indicated by most DNA-based estimates, according to new research by a UCL academic.
The research, published in Science Advances, analysed dental evolutionary rates across different hominin species, focusing on early...
The first humans who settled in Scandinavia more than 10,000 years ago left their DNA behind in ancient chewing gum, masticated lumps made from birch bark pitch. This is shown in a new study conducted at Stockholm University and...
A University of Bristol academic has succeeded where countless cryptographers, linguistics scholars and computer programs have failed—by cracking the code of the 'world's most mysterious text', the Voynich manuscript.
Although the purpose and meaning of the manuscript had eluded scholars...
Most amber inclusions are organisms that lived in the forest. It is very rare to find sea life trapped in amber. However, an international research group led by Prof. Wang Bo from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology...
A growth in the use of crystal quartz to make tools thousands of years ago shows the sophistication of ancient communities, according to new research.
The mineral was chosen because of its powerful symbolism, even though it involved painstaking work...
Abrupt climate change some 8,000 years ago led to a dramatic decline in early South American populations, suggests new UCL research.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, is the first to demonstrate how widespread the decline was and the scale at...
Statistical analysis of fossil data shows that it is unlikely that Australopithecus sediba, a nearly two-million-year-old, apelike fossil from South Africa, is the direct ancestor of Homo, the genus to which modern-day humans belong.
The research by paleontologists from the University of...
A thousand years ago, Native Americans in South America used multiple psychotropic plants—possibly simultaneously—to induce hallucinations and altered consciousness, according to an international team of anthropologists.
"We already knew that psychotropics were important in the spiritual and religious activities of...