New University of Otago research sheds light on guinea pig domestication and how and why the small, furry animals became distributed around the world.
Just published in the international science journal, Scientific Reports, the researchers use ancient DNA from archaeological guinea...
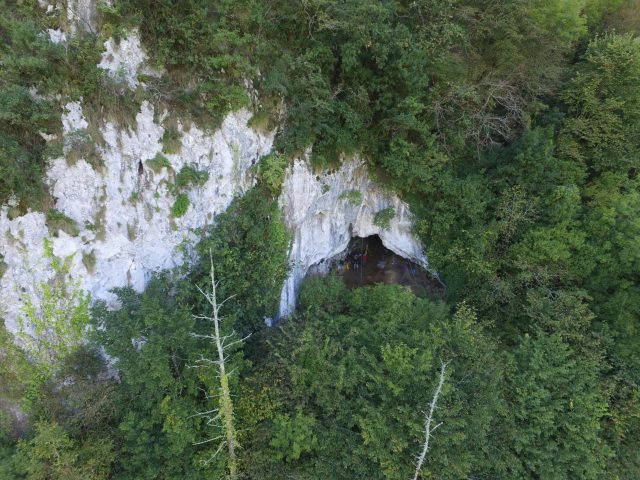
Grotte de Cussac cave in Dordogne, France, is the site of stunning cave art, containing more than 800 figurative engravings of animals and humans that are between 25,000 and 30,000 years old.
It also contains the remains of at least...
The discovery of a tiny insect fossil is unearthing big questions about the global movement of animals and the connection to changes in climate and shifting continents across deep time. The fossil, estimated to be 50 million years old,...
In contrast to the prehistoric remains of the Near East, the megalithic monuments of Arabia remain largely unknown. These monumental structures, made of dry stone walls, still hold many secrets in terms of their construction, function and chronology.
An international...
For the first time, archeologists have succeeded in mapping a complete Roman city, Falerii Novi in Italy, using advanced ground penetrating radar (GPR), allowing them to reveal astonishing details while it remains deep underground. The technology could revolutionize our...
Dating archeological objects precisely is difficult, even when using techniques such as radiocarbon dating. Using a recently developed method based on the presence of sudden spikes in carbon-14 concentration, scientists at the University of Groningen, together with Russian colleagues,...
What kind of interactions did the various Stone Age cultures have with one another? In a new interdisciplinary study, researchers have combined archaeological and genetic information to better understand Battle Axe cultural influences discovered in graves of the Pitted...
Analysis of the material on two Iron Age altars discovered at the entrance to the "holy of holies" of a shrine at Tel Arad in the Beer-sheba Valley, Israel, were found to contain Cannabis and Frankincense, according to new...
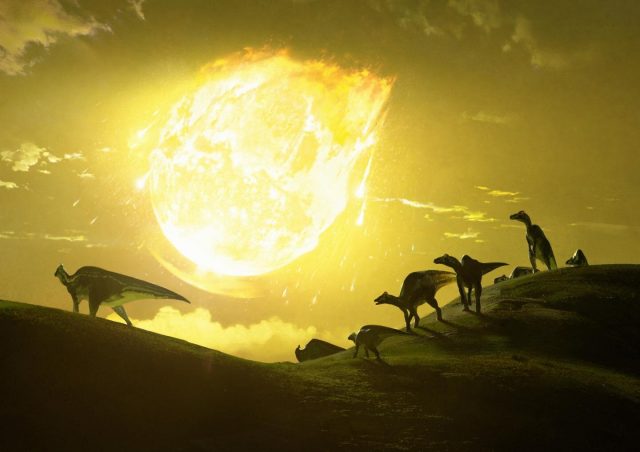
New simulations from Imperial College London have revealed the asteroid that doomed the dinosaurs struck Earth at the 'deadliest possible' angle.
The simulations show that the asteroid hit Earth at an angle of about 60 degrees, which maximised the amount...
One in three women in Europe inherited the receptor for progesterone from Neandertals—a gene variant associated with increased fertility, fewer bleedings during early pregnancy and fewer miscarriages. This is according to a study published in Molecular Biology and Evolution by researchers...
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigación sobre la Evolución Humana (CENIEH) have participated in a study published today in the journal Scientific Reports on the settlement patterns of the last Neanderthal groups in the Cantabrian region at the Amalda I...