science
Researchers achieve remote control of hormone release using magnetic nanoparticles
Abnormal levels of stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol are linked to a variety of mental health disorders, including depression and posttraumatic stress...
Simple method for ceramic-based flexible electrolyte sheets for lithium metal batteries
Researchers at Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new method to make ceramic-based flexible electrolyte sheets for lithium metal batteries. They combined a garnet-type...
Researchers move closer to producing heparin in the lab
In a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), University of California San Diego researchers moved one step closer...
Team discovers a mechanism plants use to toggle on photosynthesis
Harvesting sunlight to make energy is a complex reaction that plants do naturally, but isn't well understood.
A research team led by a Washington State...
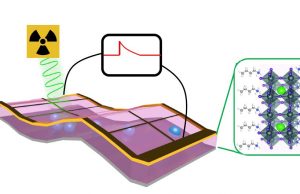
Self-powered X-ray detector to revolutionize imaging for medicine, security and research
A new X-ray detector prototype is on the brink of revolutionizing medical imaging, with dramatic reduction in radiation exposure and the associated health risks,...
New protocol identifies fascinating quantum states
Topological materials attract great interest and may provide the basis for a new era in materials development. In Science Advances, physicists around Andreas Elben, Jinlong...
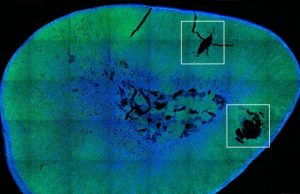
Geneticists discover regulatory mechanism of chromosome inheritance
In the course of every single cell division, the genetic information on the chromosomes must be distributed equally between the newly developing daughter cells....
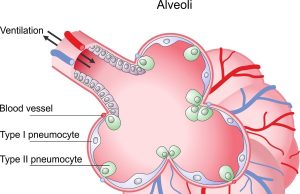
Using alveolar epithelia as a model for coronavirus infection
Before new drugs can be administered to people, researchers first have to investigate their effects using cell cultures and animal testing. Human cell cultures...
First sighting of mysterious Majorana fermion on a common metal
Physicists at MIT and elsewhere have observed evidence of Majorana fermions—particles that are theorized to also be their own antiparticle—on the surface of a...
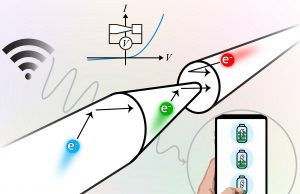
Researchers develop one-way street for electrons
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill made a one-way street for electrons that may unlock the ability for devices to...
Now metal surfaces can be instant bacteria killers
Bacterial pathogens can live on surfaces for days. What if frequently touched surfaces such as doorknobs could instantly kill them off?
Purdue University engineers have...