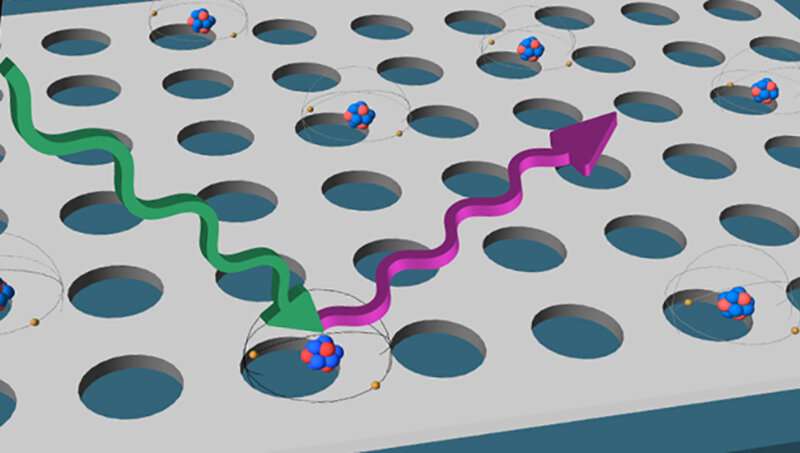
Quantum simulation more stable than expected
A localization phenomenon boosts the accuracy of solving quantum many-body problems with quantum computers. These problems are otherwise challenging for conventional computers. This brings...
SLAC develops novel compact antenna for communicating where radios fail
A new type of pocket-sized antenna, developed at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, could enable mobile communication in situations where conventional...
Research provides speed boost to quantum computers
A new finding by researchers at the University of Chicago promises to improve the speed and reliability of current and next generation quantum computers...
Earliest life may have arisen in ponds, not oceans
Primitive ponds may have provided a suitable environment for brewing up Earth's first life forms, more so than oceans, a new MIT study finds.
Researchers...
In mice, eliminating damaged mitochondria alleviates chronic inflammatory disease
Inflammation is a balanced physiological response—the body needs it to eliminate invasive organisms and foreign irritants, but excessive inflammation can harm healthy cells, contributing...
Astronaut has no lingering, major epigenetic differences from earthbound twin brother
In a landmark study, a group of U.S. scientists from Johns Hopkins, Stanford University and other institutions has found no long-lasting, major differences between...
Unique oil-eating bacteria found in world’s deepest ocean trench
Scientists from the University of East Anglia have discovered a unique oil eating bacteria in the deepest part of the Earth's oceans—the Mariana Trench.
Together...
World’s fastest hydrogen sensor could pave the way for clean hydrogen energy
Hydrogen is a clean and renewable energy carrier that can power vehicles, with water as the only emission. Unfortunately, hydrogen gas is highly flammable...
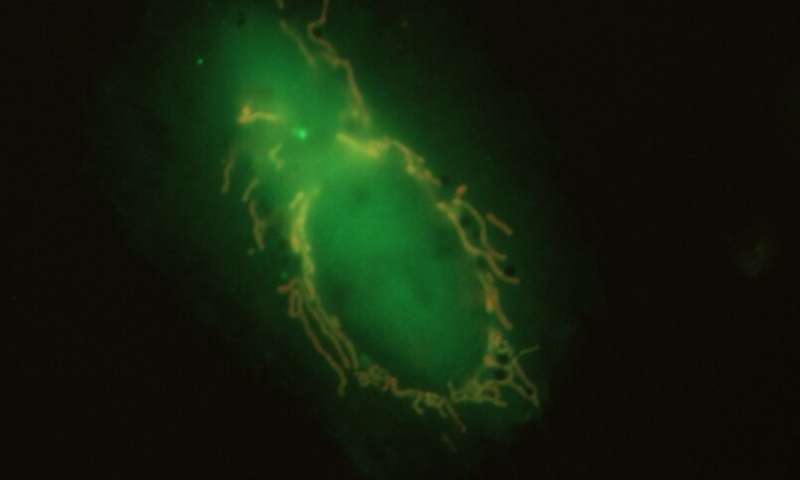
Broken mitochondria use ‘eat me’ proteins to summon their executioners
When mitochondria become damaged, they avoid causing further problems by signaling cellular proteins to degrade them. In a paper publishing April 11, 2019, in...
Ancient DNA reveals new branches of the Denisovan family tree
It's widely accepted that anatomically modern humans interbred with their close relatives, the Neanderthals and Denisovans, as they dispersed out of Africa. But a...
Team makes artificial atoms that work at room temp
Ultra-secure online communications, completely indecipherable if intercepted, is one step closer with the help of a recently published discovery by University of Oregon physicist...