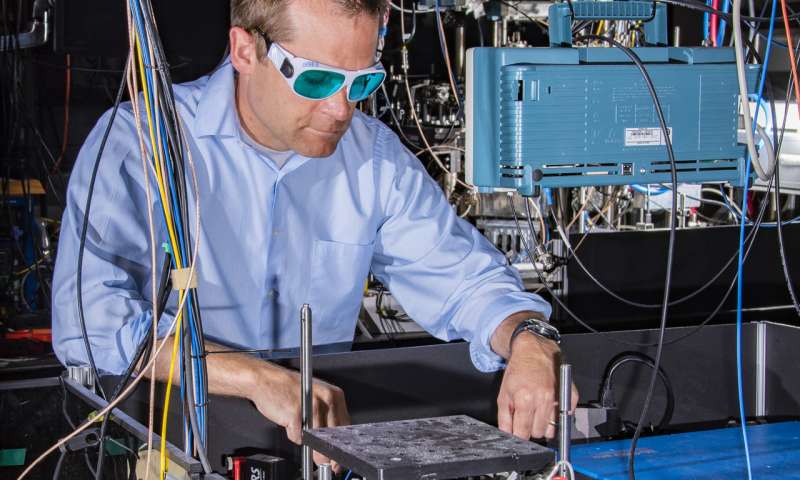
High-speed camera shows incoming particles cause damage by briefly melting surfaces as they strike
When tiny particles strike a metal surface at high speed—for example, as coatings being sprayed or as micrometeorites pummeling a space station—the moment of...
New catalyst material produces abundant cheap hydrogen
QUT chemistry researchers have discovered cheaper and more efficient materials for producing hydrogen for the storage of renewable energy that could replace current water-splitting...
Fossil algae reveal 500 million years of climate change
Earth scientists are able to travel far back in time to reconstruct the geological past and paleoclimate to make better predictions about future climate...
Atomic jet—the first lens for extreme-ultraviolet light developed
Scientists from the Max Born Institute (MBI) have developed the first refractive lens that focuses extreme ultraviolet beams. Instead of using a glass lens,...
NIST atomic clocks now keep time well enough to improve models of Earth
Experimental atomic clocks at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have achieved three new performance records, now ticking precisely enough to not...
Study unlocks full potential of ‘supermaterial’ graphene
New research reveals why the "supermaterial" graphene has not transformed electronics as promised, and shows how to double its performance and finally harness its...
Fires fueled spread of grasslands on ancient Earth
Ancient wildfires played a crucial role in the formation and spread of grasslands like those that now cover large parts of the Earth, according...
Flexible electronic skin aids human-machine interactions
Human skin contains sensitive nerve cells that detect pressure, temperature and other sensations that allow tactile interactions with the environment. To help robots and...
Potential arthritis treatment prevents cartilage breakdown
Osteoarthritis, a disease that causes severe joint pain, affects more than 20 million people in the United States. Some drug treatments can help alleviate...
First risk genes for ADHD found
A major international collaboration headed by researchers from the Danish iPSYCH project, the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT, Massachusetts General Hospital, SUNY Upstate...
Atomic clocks now keep time well enough to improve models of Earth
Experimental atomic clocks at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have achieved three new performance records, now ticking precisely enough to not...