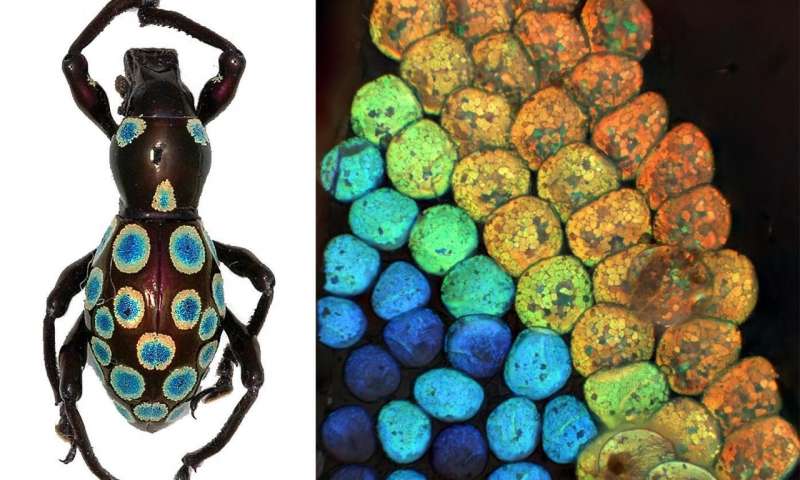
A new method to produce large, monolayer single-crystal-like graphene films more than a foot long relies on harnessing a "survival of the fittest" competition among crystals. The novel technique, developed by a team led by the Department of Energy's...
An atypical two-dimensional sandwich has the tasty part on the outside for scientists and engineers developing multifunctional nanodevices.
An atom-thin layer of semiconductor antimony paired with ferroelectric indium selenide would display unique properties depending on the side and polarization by an external...
Nanomaterials could provide the basis of many emerging technologies, including extremely tiny, flexible, and transparent electronics.
While many nanomaterials exhibit promising electronic properties, scientists and engineers are still working to best integrate these materials together to eventually create semiconductors and circuits...
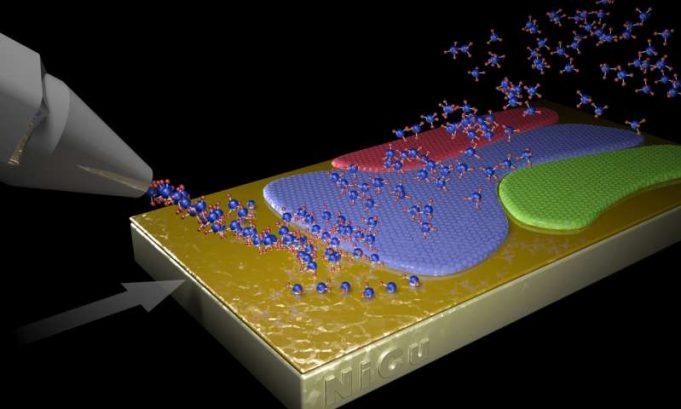
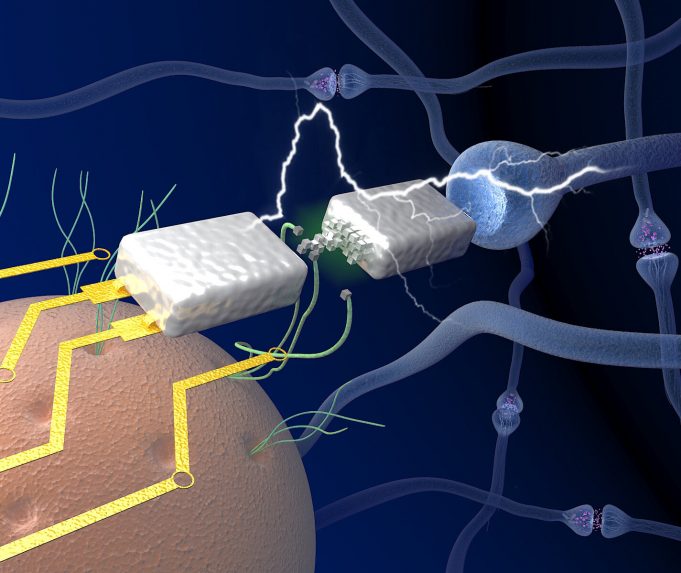
Targeting medical treatment to an ailing body part is a practice as old as medicine itself. A Band-Aid is placed on a skinned knee. Drops go into itchy eyes. A broken arm goes into a cast.
But often what ails...
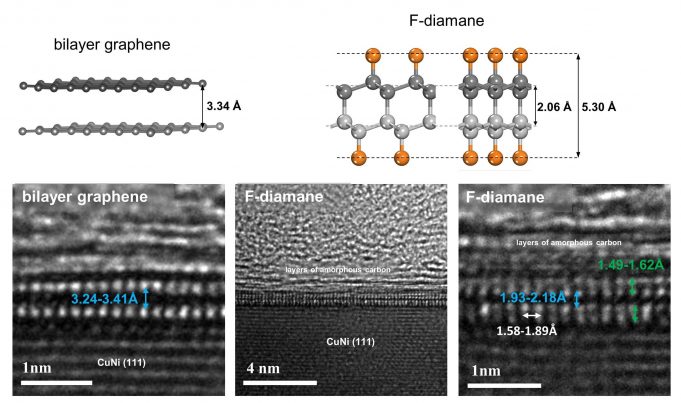
Can two layers of the "king of the wonder materials," i.e. graphene, be linked and converted to the thinnest diamond-like material, the "king of the crystals?" Researchers of the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM) within the Institute for...
Researchers from Yale-NUS College and the University of Fribourg in Switzerland have discovered a novel colour-generation mechanism in nature, which if harnessed, has the potential to create cosmetics and paints with purer and more vivid hues, screen displays that...
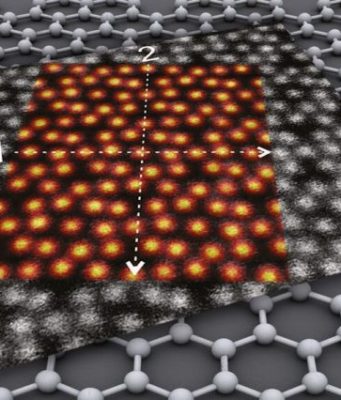
Graphene—an ultrathin material consisting of a single layer of interlinked carbon atoms—is considered a promising candidate for the nanoelectronics of the future. In theory, it should allow clock rates up to a thousand times faster than today's silicon-based electronics....
Only 10 years ago, scientists working on what they hoped would open a new frontier of neuromorphic computing could only dream of a device using miniature tools called memristors that would function/operate like real brain synapses.
But now a team...
Scientists have visualised the electronic structure in a microelectronic device for the first time, opening up opportunities for finely-tuned high performance electronic devices.
Physicists from the University of Warwick and the University of Washington have developed a technique to measure...
Scientists have developed a method to use lasers to control the movement of nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers.
Scientists have long been working on improving their ability to use lasers to move small objects without actually touching them. This method of...
Freestanding clusters of 20 gold atoms take the shape of a pyramid, researchers have discovered. This is in contrast with most elements, which organize themselves by forming shells around one central atom. The team of researchers led by KU...