COVID-19 report, photo concept (stock image).Credit: © Milos / stock.adobe.com
The COVID-19 pandemic, which claimed more than 336,000 lives in the United States in 2020, has significantly affected life expectancy, USC and Princeton researchers have found.
The researchers project that, due...
An important and still unanswered question is how new genes that cause antibiotic resistance arise. In a new study, Swedish and American researchers have shown how new genes that produce resistance can arise from completely random DNA sequences. The...
Wistar Institute scientists have discovered a new class of compounds that uniquely combine direct antibiotic killing of pan drug-resistant bacterial pathogens with a simultaneous rapid immune response for combatting antimicrobial resistance (AMR). These finding were published today in Nature.
The World...
During the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, Joseph Lee McCauley, a physics professor at the University of Houston, was watching the daily data for six countries and wondered if infections were really growing exponentially. By extracting the doubling...
Many people wear masks in public to slow the spread of COVID-19, as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). However, masks with exhalation valves do not slow the spread of the disease, and now, new...
In the nearly two centuries since German physician Carl Wunderlich established 98.6°F (37 C) as the standard "normal" body temperature, it has been used by parents and doctors alike as the measure by which fevers—and often the severity of...
In a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), University of California San Diego researchers moved one step closer to the ability to make heparin in cultured cells. Heparin is a potent anti-coagulant and...
Scientists can now edit multiple sites in the genome at the same time to learn how different DNA stretches co-operate in health and disease.
CRISPR-based DNA editing has revolutionized the study of the human genome by allowing precise deletion of...
A highly sensitive, wearable gas sensor for environmental and human health monitoring may soon become commercially available, according to researchers at Penn State and Northeastern University.
The sensor device is an improvement on existing wearable sensors because it uses a self-heating mechanism that enhances...
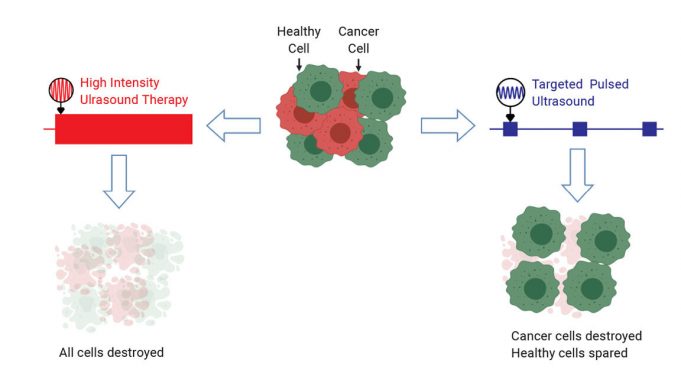
Doctors have used focused ultrasound to destroy tumors without invasive surgery for some time. However, the therapeutic ultrasound used in clinics today indiscriminately damages cancer and healthy cells alike.
Most forms of ultrasound-based therapies either use high-intensity beams to heat...
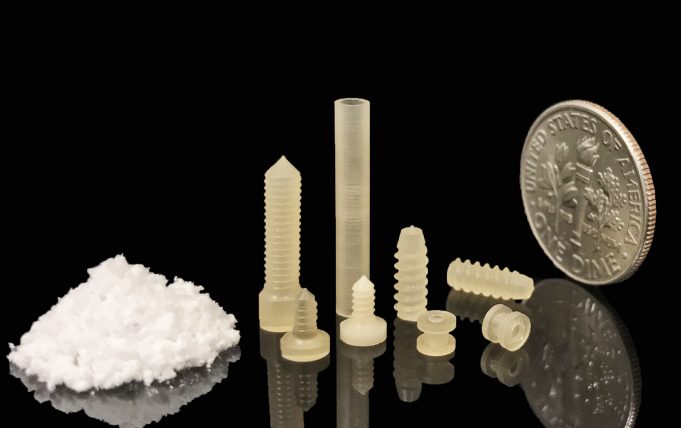
Researchers led by engineers at Tufts University have developed a novel, significantly more efficient fabrication method for silk that allows them to heat and mold the material into solid forms for a wide range of applications, including medical devices....